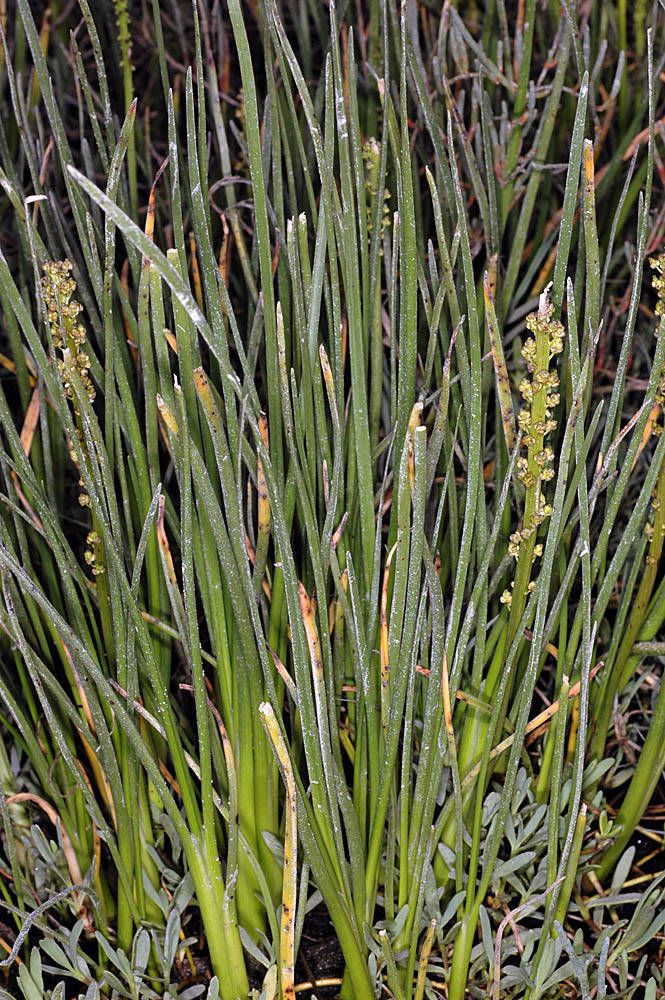
Triglochin maritima
seaside arrow-grass
elliptical in cross section, 22–60 cm × 2–5 mm;
ligules entire to notched, 1–2 mm.
racemes exceeding leaves, 45–130 cm.
ascending, 2–6 mm.
tepals 1.5–2 mm, fertile carpels 6.
schizocarps, oblong, 3–5 mm.
=12, 24, 30, 36, 48, 60, 120, 144.
Triglochin maritima
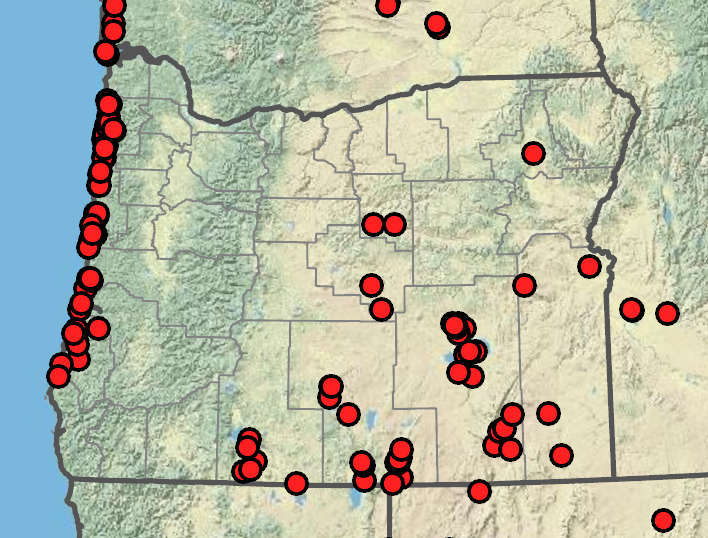
Coastal salt and inland freshwater marshes and moist meadows, especially brackish, saline, or alkaline areas. Flowering Apr–Aug. 0–1700m. BR, BW, CR, ECas, Est, Owy. CA, ID, NV, WA; throughout North America; South America; Asia, Europe. Native.
Triglochin concinna and T. maritima are frequently considered the same species; the treatment in Flora of North America synonymizes T. concinna with T. maritima (Haynes and Hellquist 2000). Both species produce a cyanide-containing sugar called triglochinin, which can poison livestock when eaten in large amounts. Production is highest in the spring (Majak et al. 1980), and because the compound remains potent in a dried state, care should be taken to prevent inclusion of young Triglochin in hay bales.
Rachel Newton
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search