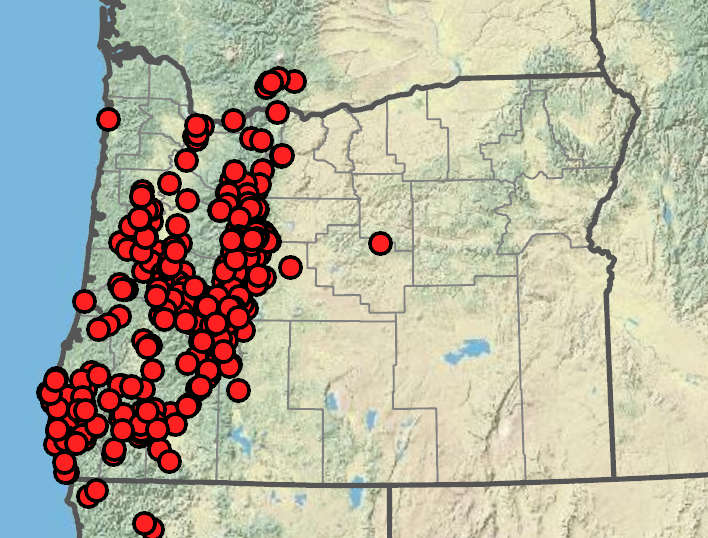
Cirsium remotifolium
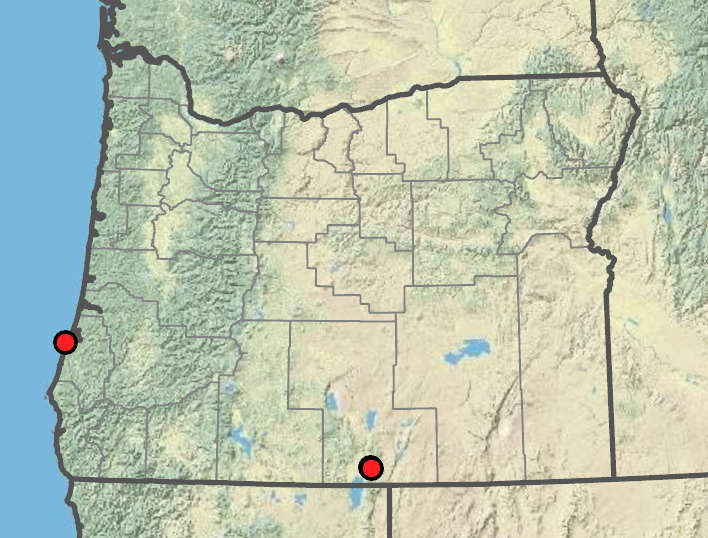
Cirsium andersonii
few-leaved thistle, weak thistle
Anderson's thistle
usually 1; slender, arachnoid-villous, sometimes thinly so.
usually 1, sparsely arachnoid-tomentose to glabrate.
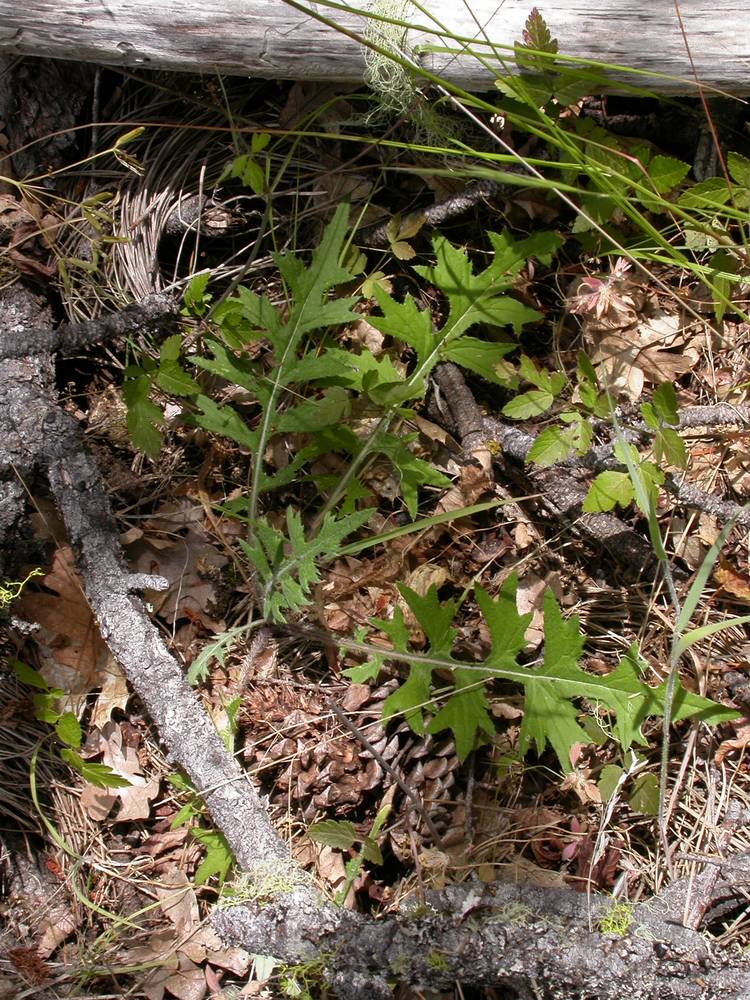
linear-oblong to elliptic, 7–35 × 1–15 cm;
margins entire to dentate or pinnately lobed;
lobes triangular-ovate to linear;
spines fine, 1–6 mm;
surfaces abaxially thinly to densely tomentose, adaxially glabrate to thinly arachnoid-villous;
basal occasionally present at flowering, sessile, clasping, or petiolate.
elliptic to linear-oblong, 8–20(35) × 2–8 cm, gradually reduced above;
margins coarsely dentate or 1–2-pinnate;
spines 1–5 mm;
surfaces abaxially ± thinly gray-tomentose, adaxially glabrous to sparsely pilose;
basal usually present at flowering, clasping to petiolate.
hemispheric to campanulate, 1–2.5 × 1.5–3.5 cm, glabrous to thinly arachnoid-villous.
broadly cylindric to narrowly campanulate, 3–5 × 2–4 cm, glabrous to thinly tomentose.
corollas 16–25 mm, cream-colored to purple;
tubes 6–12 mm;
throats 5–10.5 mm;
lobes 3.5–8 mm;
styles conspicuously exserted;
tips 4–6 mm.
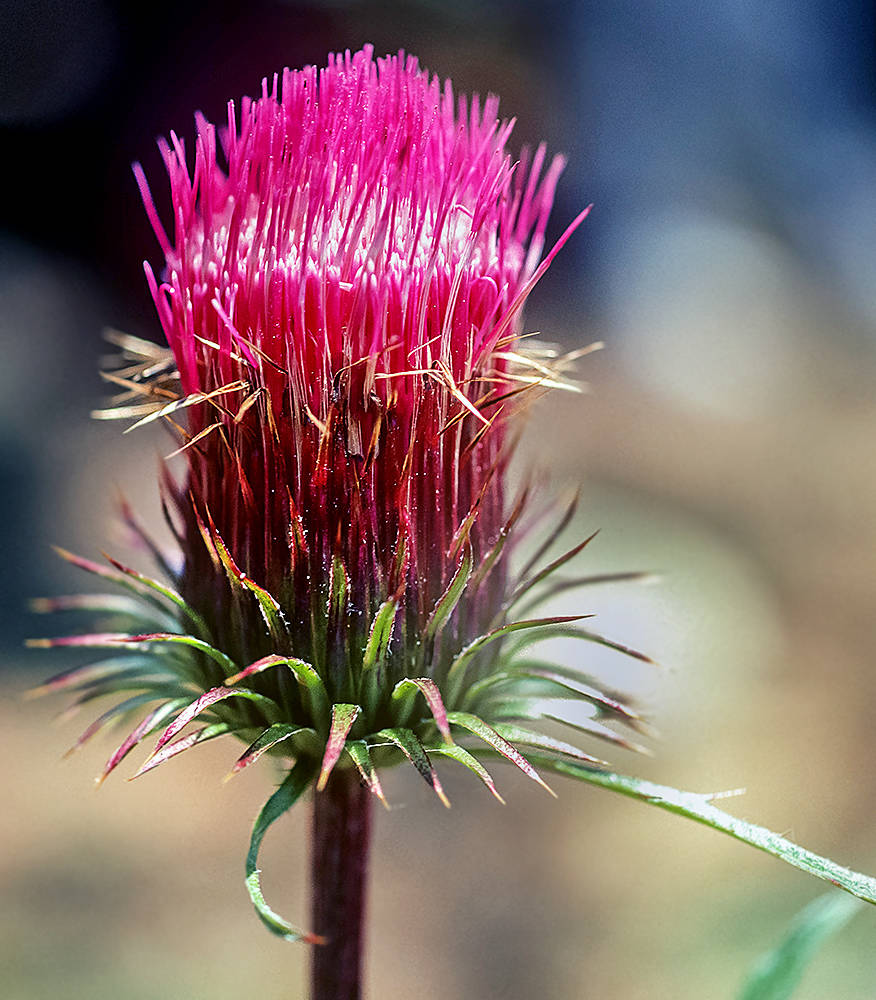
corollas 30–45 mm, red, occasionally red-purple;
tubes 10–20 mm;
throats abruptly narrowed to tubes, 10–16 mm;
lobes 9–11 mm;
styles conspicuously exserted;
tips 3.5–5 mm, sometimes geniculate.
subequal to strongly imbricate, sometimes with inconspicuous glutinous ridges;
spines 1–6 mm; outer bases ? 2 mm wide.
without glutinous ridges;
spines weak, 1–3 mm; outer short, linear-lanceolate, appressed;
margins entire or spiny-ciliate;
tips long-acuminate; inner linear; long; entire;
tips red to purple; flat.
4.5–5.5 mm, tan to dark brown;
pappi 12–25 mm.
6–7 mm, brown;
pappi 25–40 mm.
few–many.
1–6 per branch;
lateral heads widely spaced along distal portions of branches.
Cirsium remotifolium
Cirsium andersonii
Western United States. 3 varieties.
Cirsium remotifolium is known to form fertile hybrids with C. edule where their ranges overlap.
Open grasslands, montane woodlands. Flowering Jul–Sep. 1500–2500 m. ECas. CA, NV. Native.
Cirsium andersonii, while currently rare in Oregon, is well documented in northern California and Nevada.
Bridget Chipman
Bridget Chipman
- Local floras:
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search