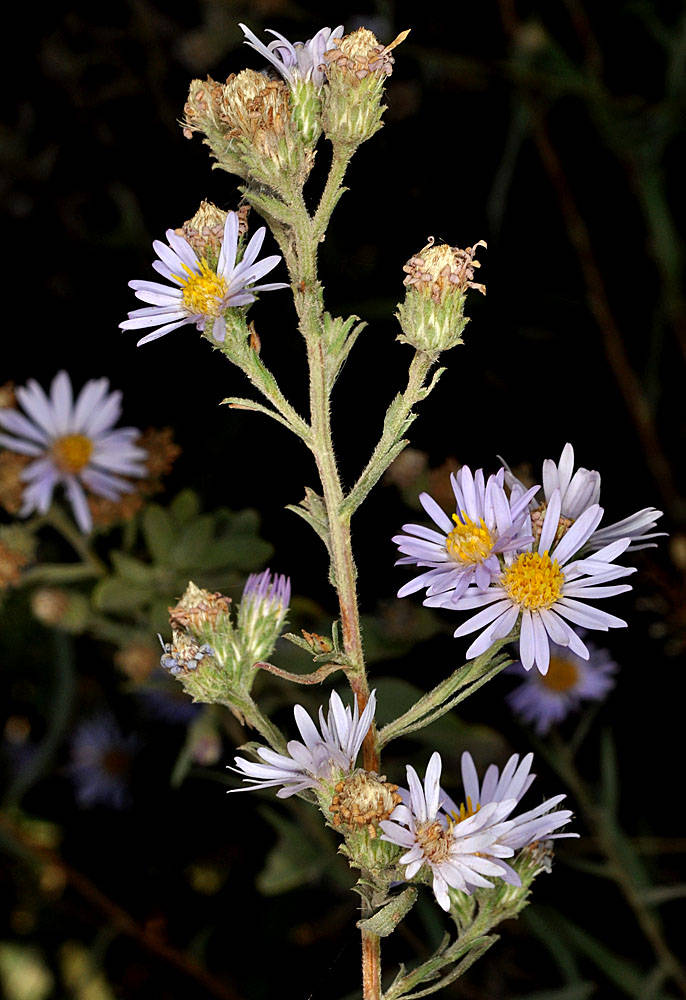
Symphyotrichum spathulatum
Symphyotrichum
western mountain aster
aster
ascending to erect, glabrous to sparsely pubescent.
generally erect, glabrous to densely pubescent, sometimes glandular-pubescent.
? 7 × as long as wide;
margins entire;
tips acute;
surfaces glabrous to sparsely puberulent;
basal leaves present at flowering, narrowly elliptic to obovate, 5–15 cm, petiolate;
cauline linear to narrowly elliptic, 3–6(12) cm, subpetiolate to sessile.
basal and cauline, alternate, linear to lanceolate or elliptic or obovate, generally entire;
basal leaves senescent or persistent at flowering, petiolate to sessile.
open; panicle-like arrays, usually few-branched.
compact to open panicle- or raceme-like arrays;
branches usually bracteolate.
5–10 mm.
cylindrical to campanulate.
flat to slightly convex;
paleae 0.
15–40;
rays 9–15 mm, violet.
(0)10–50(100), pistillate;
rays white to pink or violet-purple.
(6)10–50(100); bisexual;
corollas yellow, tubular;
tubes < throats;
lobes triangular; erect or reflexed.
in 3–5 unequal series, linear to narrowly oblanceolate, bases scarious-margined;
tips acute, sometimes ± obtuse, green;
surfaces glabrous to sparsely puberulent.
in 3–6 series, appressed to spreading, imbricate to subequal or outer bracts longer, bases with pale scarious margins and tips green, or the outer foliaceous and green throughout.
pubescent;
pappus bristles 5–7 mm; whitish.
obconic; somewhat flattened, 3–5-veined, brown to purplish;
pappi of (20)25–40 barbellate bristles in 1 series.
3–50.
radiate or rarely discoid.
Symphyotrichum spathulatum
Symphyotrichum
3 varieties.
Asia, North America, South America. ~90 species; 15 species treated in Flora.
Symphyotrichum is well known for its taxonomic difficulty, a reflection of multiple factors including the prevalence of polyploid complexes (in Oregon, mainly involving species with n=8) and the influence of phenology and environment on many morphological characters. Symphyotrichum novae-angliae, an occasional garden escape, is separable from S. campestre by its larger heads with usually 50–75 rays (versus 15–30 rays for S. campestre).
Geraldine Allen
Geraldine Allen
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search