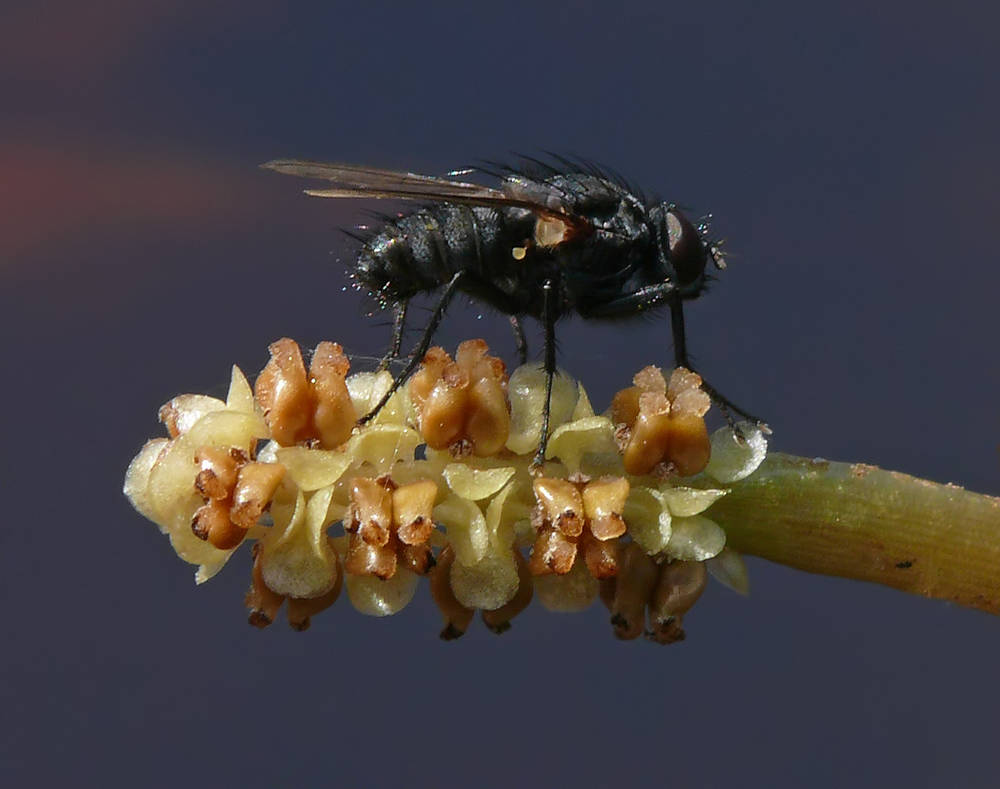
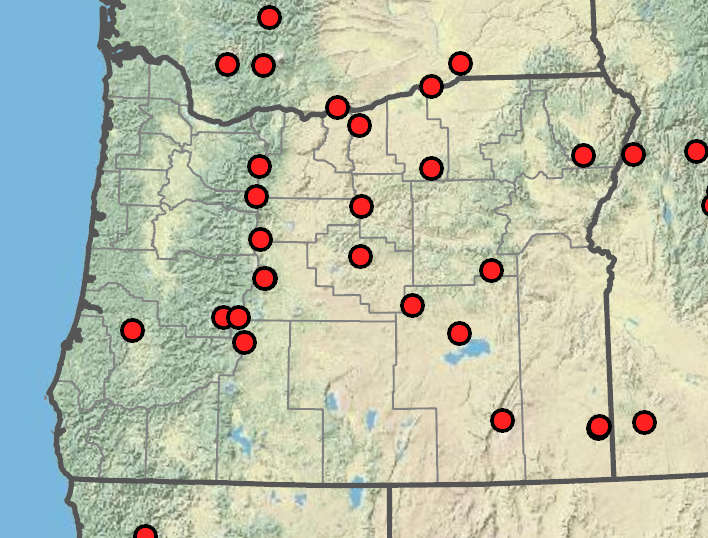
Potamogeton alpinus
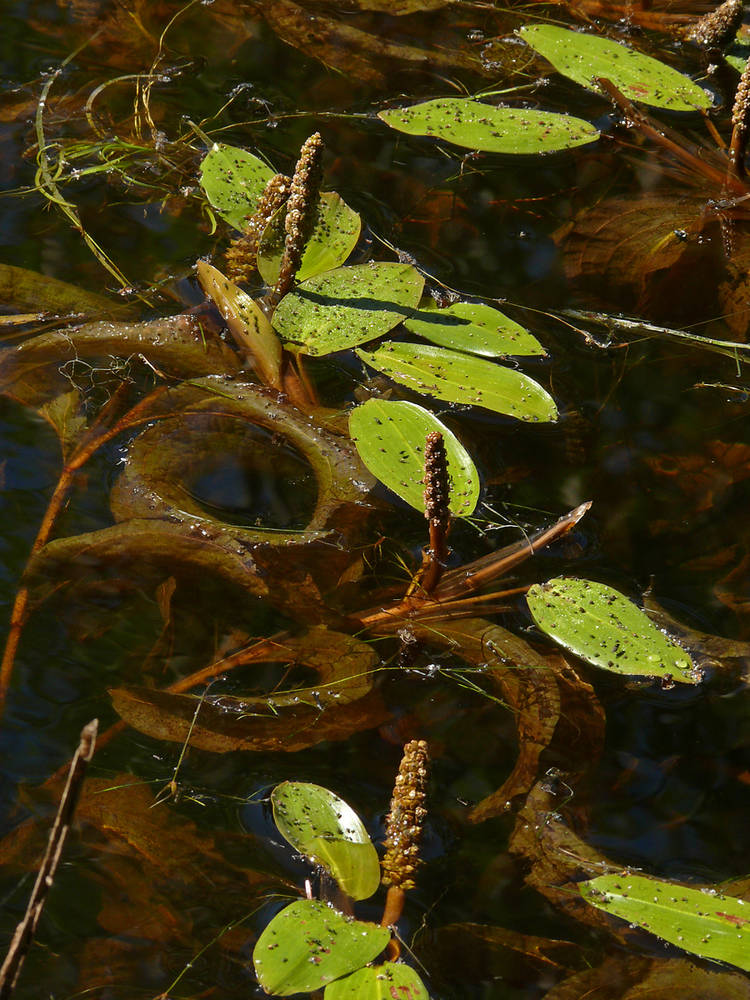
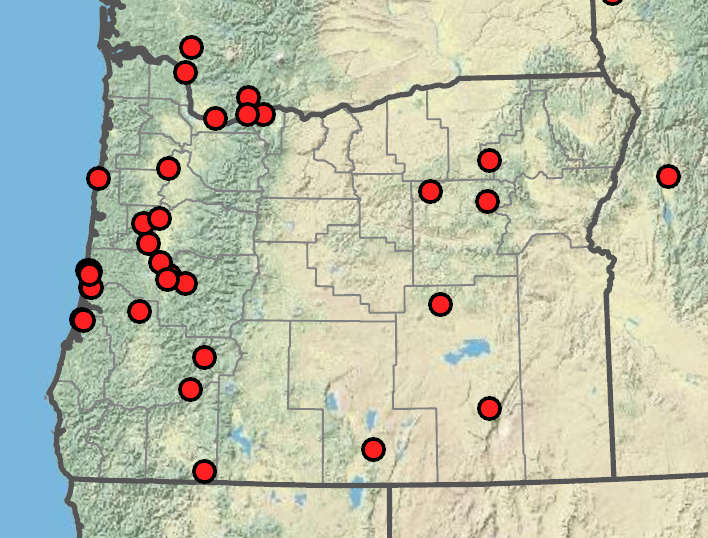
Potamogeton amplifolius
northern pondweed, reddish pondweed
broad-leaved pondweed, large-leaved pondweed
terete; to 200 cm; nodal glands absent.
terete, 6–110 cm; nodal glands absent.
submersed and floating or submersed only.
submersed and floating or rarely submersed only.
elliptic or oblanceolate to obovate or oblonglinear, 40–70(100) × 10–25(40)mm; reddish green;
base gradually tapering to petiole;
tip obtuse or acute;
veins (7)9–13(15);
petioles 0–12 mm.
lanceolate to round elliptic, 43–92 × 25–38 mm, light green;
base rounded to cordate;
tip acute to rounded;
veins 27–49;
petioles 23–226 mm.
sessile, attached to stem nodes, not attached to stipules;
stipules (12)15–25(40)mm;
tip blunt;
blades oblong-linear to linear-lanceolate, 45–180(250) × 5–20 mm;
base rounded to cuneate;
margins entire;
tip obtuse or acute; lacunae in 0–6 rows on each side of midvein;
veins 7–9.
petiolate, attached to stem nodes, not attached to stipules;
stipules 15–117 mm;
tip acute;
blades ovate to oblanceolate, distinctly falcate, 50–125 × 15– 58 mm;
base rounded to acute;
margins entire and recurved; wavy;
tip acute to round-apiculate;
veins 19–49;
petioles terete, 0.9–11.5 cm.
emersed;
spikes cylindric, 10–35 mm;
peduncles terminal or axillary; erect, 30– 100(160)mm.
emersed;
spikes cylindric, 34–65 mm;
peduncles terminal or axillary; erect, cylindric, 45–223 mm.
pedicellate, obovoid; turgid; (2.5)3–3.5 × (1.7)2–2.4 mm, dorsally keeled, laterally keeled or not;
beaks dorsally curved, 0.5–0.9 mm.
sessile, obovoid; turgid, 5–6.7 × 4.5–5.2 mm; reddish brown, dorsally keeled, laterally ridged;
beaks erect, 0.5–0.8 mm.
Potamogeton alpinus
Potamogeton amplifolius
Ponds, lakes, and slow-moving streams. 1200–2200m. BR, BW, Casc. CA, ID, NV, WA; north to British Columbia, east to Greenland; Eurasia. Native.
Potamogeton alpinus is often red when fresh. This species hybridizes with P. nodosus, P. gramineus, and P. praelongus.
Lakes, ponds, streams. 0–2100m. BR, BW, Casc, CR, ECas, Est, WV. CA, ID, WA; north to British Columbia, east to Newfoundland. Native.
Potamogeton amplifolius has large submersed leaves that are folded and falcate and have numerous veins. This species hybridizes with P. illinoensis.
Nick Otting, Richard Brainerd, Barbara Wilson
Nick Otting, Richard Brainerd, Barbara Wilson
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search