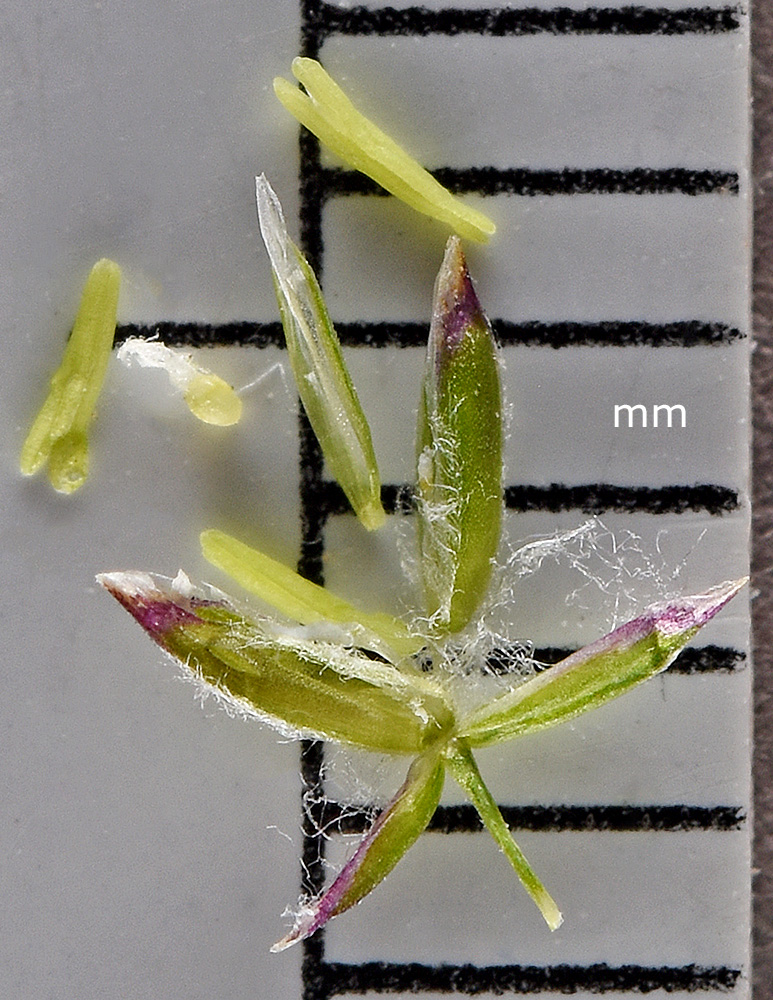
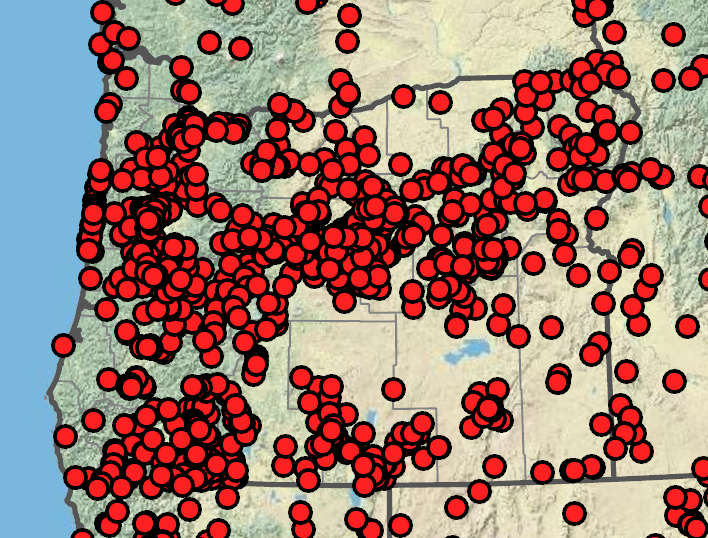
Poa pratensis
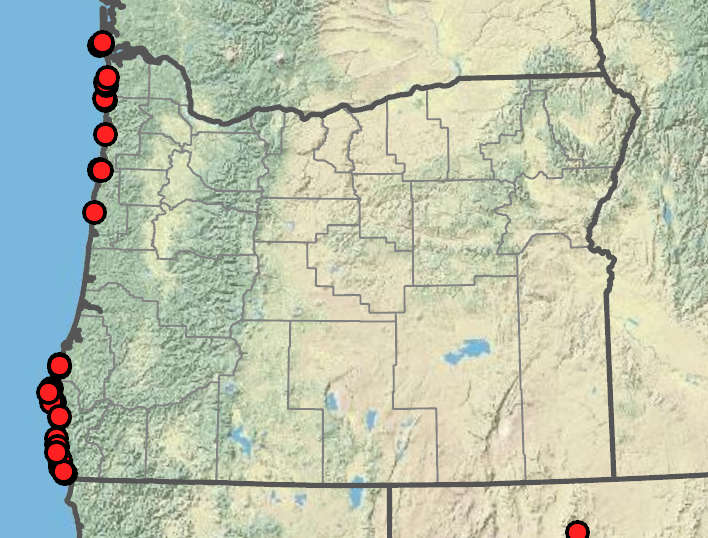
Poa unilateralis
Kentucky bluegrass
San Francisco bluegrass
nodes terete or slightly compressed, 1–2(3) nodes exposed.
mainly extravaginal or equally extra- and intravaginal.
intra- and extravaginal or mainly intravaginal.
sheaths closed 25–50% of their length, bases of basal sheaths glabrous;
collars smooth, glabrous;
ligules truncate to rounded, 0.9–2(3.1)mm, blades of extravaginal shoots like cauline blades, those of intravaginal shoots; when present, sometimes distinctly narrower; flat to involute, 0.4–1 mm wide;
cauline blades flat or folded; to involute on the margins, 0.4–4.5 mm wide;
lower surfaces smooth, glabrous;
upper surfaces smooth or sparsely scabrous, frequently with sparse; slender hairs 0.2–0.8 mm long; uppermost blades 1.5–10 cm.
sheaths closed 10(20)% of their length, bases of basal sheaths glabrous;
ligules (0.8)2–6 mm long, blades of tillers usually 1–1.5 mm wide; thin; soon withering, distinctly narrower than those of the culm, infrequently broad and flat, or involute;
cauline blades flat or folded, 2–5 mm wide; soft; thin and soon withering or moderately thick and somewhat fleshy and retaining their form; smooth;
blades gradually reduced in length higher on the culm.
narrowly ovoid to narrowly or broadly pyramidal, loosely contacted to open, sparsely to moderately congested, 2–15(20)cm;
spikelets (25)30–100+;
branches spreading; (1)2–9 cm long; (1)2–7(9) per node;
spikelets 4–30(50), usually fairly crowded in distal half.
erect, nearly cylindrical, contracted, 3–7 cm;
spikelets (20)30–80(120);
branches 0.5–1.5(4.5)cm long, 3–7 per node, densely papillose and sparsely scabrous.
lanceolate to narrowly ovate; to 3.5 times as long as wide, 4.5–7 mm;
florets 3–5.
lanceolate, slightly unequal;
keels smooth and papillate or scabrous;
lower glumes 3-veined.
glabrous or with a crown of tiny crisp hairs around the base;
hairs 0.1–0.2 mm long.
lanceolate, distinctly keeled, 3–4.5 mm, glabrous, or keels and marginal veins short-villous on proximal half, sparsely crisply puberulent near the base;
margins glabrous;
tips acute.
1.5–3 mm.
Poa pratensis
Poa unilateralis
6 subspecies; 5 subspecies treated in Flora.
Poa pratensis is a common grass with slightly nodding inflorescences and copious cobwebby callus hairs. Poa rhizomata, of rocky ultramafic slopes in southwestern Oregon, is similar but has sparse inflorescences, acute ligules, and unisexual inflorescences. Poa confinis of coastal sands has glabrous (to sparsely hairy) lemmas and diffuse, not tufted callus hairs. Poa wheeleri, a common eastern Oregon species, lacks the lemma hairs and has denser inflorescences and more strongly scabrous leaf sheaths. Poa pratensis is common, polyploid, and highly variable. It hybridizes with related taxa including P. alpina, P. secunda, and P. wheeleri. The resulting variation in P. pratensis can be perpetuated through both sexual and asexual seed production, resulting in many recognizable forms that are linked by intermediates. Most or all Poa pratensis found in Oregon are descended from three introduced subspecies (P. p. ssp. angustifolia, P. p. ssp. pratensis, and P. p. ssp. irrigata).
2 subspecies.
Poa unilateralis is a cespitose grass with dense inflorescences that grows on coastal headlands. Its leaf sheaths are open most of their length, and its calluses are glabrous or nearly so.
Rob Soreng, Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
Rob Soreng, Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
- Local floras:
BC,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search