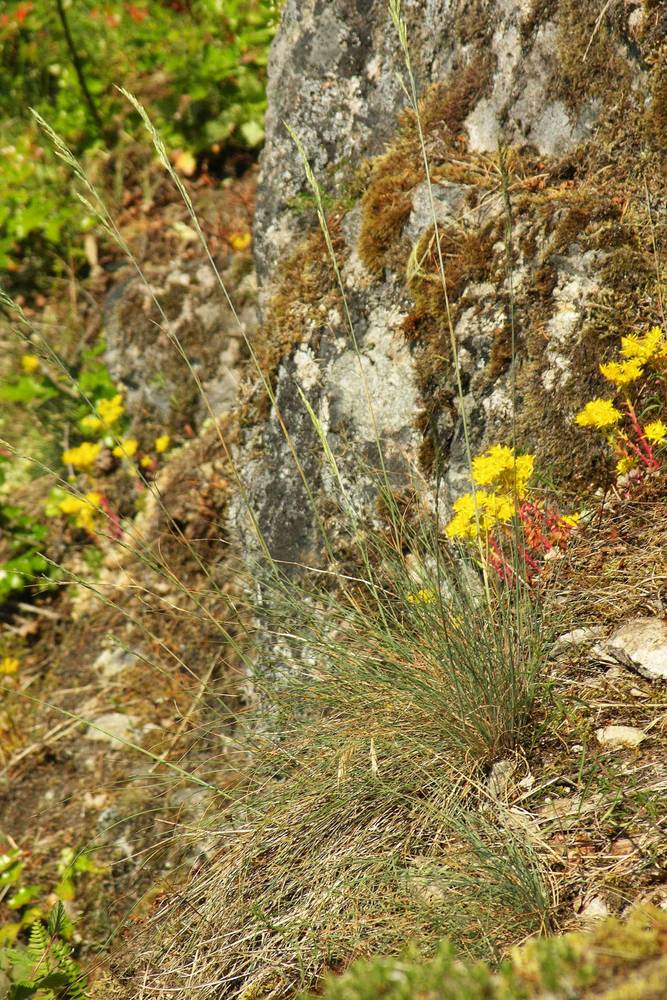
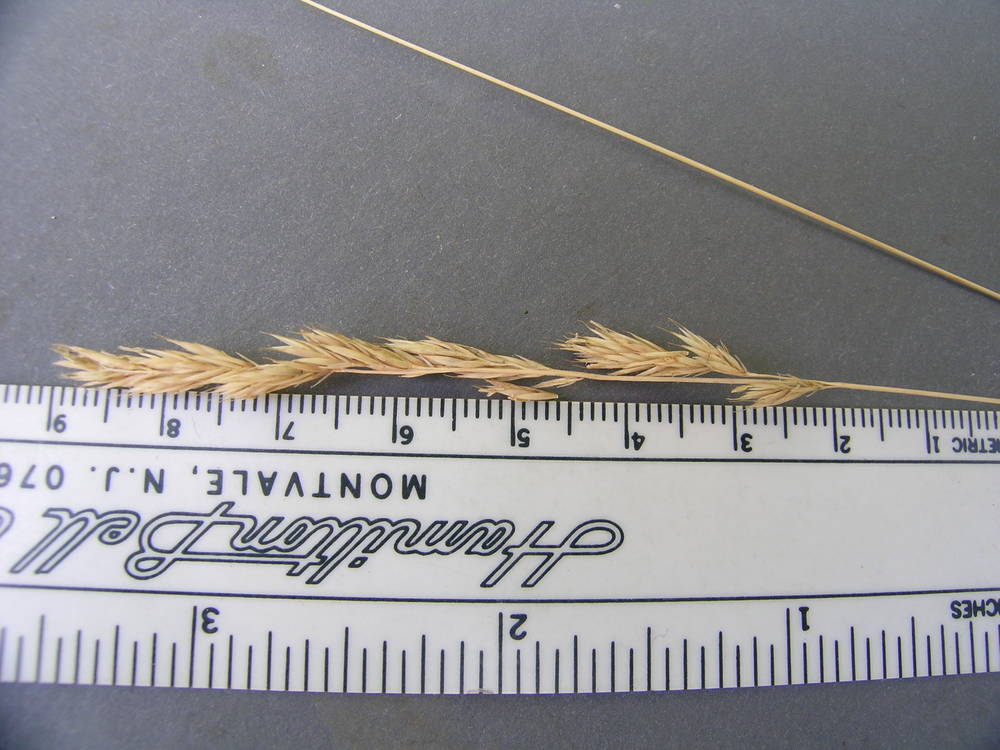
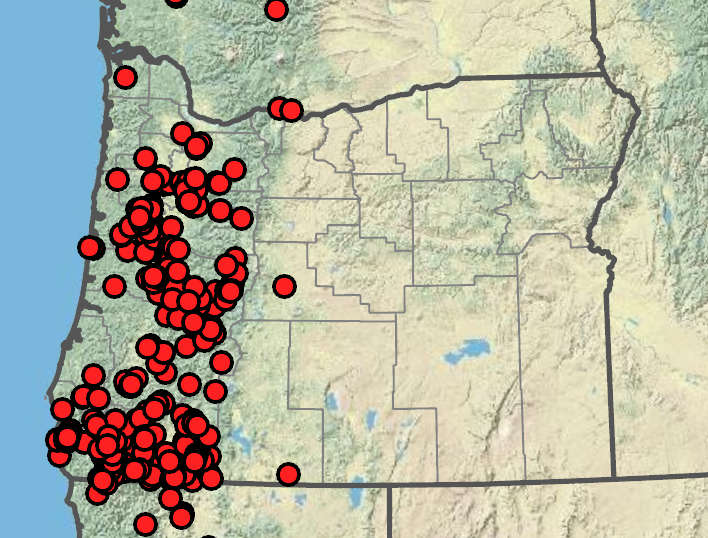
Festuca roemeri
Festuca trachyphylla
Roemer's fescue
hard fescue, sheep fescue
basal branching intravaginal.
intravaginal.
mainly basal;
sheaths open, glabrous but sometimes hairy, not conspicuously splitting between the veins, usually pale, becoming gray-brown with age;
collars glabrous;
ligules 0.1–0.4 mm;
blades 15–35 cm × 0.5–1.2(2.5)mm, conduplicate or occasionally flat;
outer surface usually glabrous, sometimes hairy;
inner surface glabrous, scabrous; hairy; flag leaves 7–12(18) cm.
mainly basal;
sheaths open; somewhat flattened, not conspicuously splitting between the veins;
blades 8–30 cm × 0.3–1.2 mm, conduplicate;
inner surface with minute hairs that are much shorter than the leaf is thick;
outer surface glabrous or tomentose.
(8)10–20(25)cm;
branches 3–7 cm, ascending to reflexed at anthesis, appressed after anthesis or sometimes the lowest spreading to reflexed.
3–10(30) cm;
branches 1.2– 3.6 cm, appressed after anthesis.
9.5–12(13.5)mm, 3–6 florets.
5.5–9(10) mm, 4–7(8) florets.
glabrous or scabrous to short-hairy at the tip only;
lower glumes 2–5 mm, 1-veined;
upper glumes 4–5.5(6.2)mm, 3-veined.
scabrous at the tip and often along the midrib;
lower glumes 2–4 mm, 1–3-veined;
upper glumes 3–5.5 mm, 3-veined.
glabrous.
2.5–3.5 mm, glabrous.
apex glabrous.
apex glabrous.
cross sections usually 0.4–0.8 × 0.75–1.2 mm, elliptic or L-shaped;
veins (5)7(10);
ribs 5(9); dorsal sclerenchyma bands more than 2 times wider than thick, sometimes restricted to the midrib and margins only.
cross sections 0.4–0.6 × 0.7–1.2 mm, elliptic or ovate;
veins (5)7+;
ribs 1–5; dorsal sclerenchyma bands more than 2 times as wide as thick, interrupted or continuous.
(5.8)6.5–8.2 mm, 0(5)-veined, with hairs on the distal part only;
lemma awns 2–4(5)mm; shorter than or as long as the lemma body.
(3.8)4–5(5.5)mm, 0(1)-veined, glabrous, scabrous, or with long hairs on margins near tip;
lemma awns 0.5–2.5 mm, usually less than half as long as the lemma body.
3–5 mm.
(1.6)2–3(3.4)mm.
=28.
=28, 42.
Festuca roemeri
Festuca trachyphylla
2 varieties.
Festuca roemeri is most often confused with the bunchgrass forms of F. rubra. Festuca rubra leaves are smooth, the sheath margins are fused, and bunchgrass forms of F. rubra usually have shorter lemmas. In cross section, leaves of sterile shoots of F. rubra are diamond shaped to triangular, angled next to the largest lateral veins. The leaf sclerenchyma bands are less than twice as wide as thick. Festuca roemeri is closely related to F. idahoensis, and intermediate plants can be found where the ranges of the two species come into contact at the east end of the Columbia Gorge, in the High Cascades, and in Klamath County. Festuca idahoensis has round to hexagonal leaves that spin readily between one’s thumb and forefinger. Festuca roemeri leaves usually won’t roll, though leaves from very dry serpentine sites will roll but with the angles easily felt. Festuca trachyphylla and F. valesiaca have smaller lemmas and denser inflorescences. Vegetative F. valesiaca cannot be distinguished from F. roemeri.
Roadsides, disturbed areas, ski slopes, persisting from cultivation or where planted for erosion control, occasionally naturalizing. 0–2800m. BR, BW, Casc, Lava, Sisk, WV. CA, WA; scattered throughout North America; worldwide. Exotic.
Festuca trachyphylla is a fine-leaved bunchgrass with small lemmas and dense inflorescences.Festuca idahoensis and F. roemeri have longer lemmas and more open inflorescences, at least at anthesis. Festuca rubra ssp. commutata has fused leaf sheath margins and leaves that are diamond-shaped in cross section with sclerenchyma bundles less than twice as broad as thick. Festuca valesiaca is very similar but has tighter, less conspicuous leaf sheaths; F. trachyphylla and F. valesiaca are best distinguished by leaf anatomy. The glaucous forms of Festuca trachyphylla are often called sheep fescues and labeled F. ovina, but the name F. ovina is best limited to a species of northern Europe and few cultivars are derived from it. The hard and sheep fescues are sometimes considered part of F. longifolia, but current usage limits that name to a British species, which is rarely cultivated.
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search