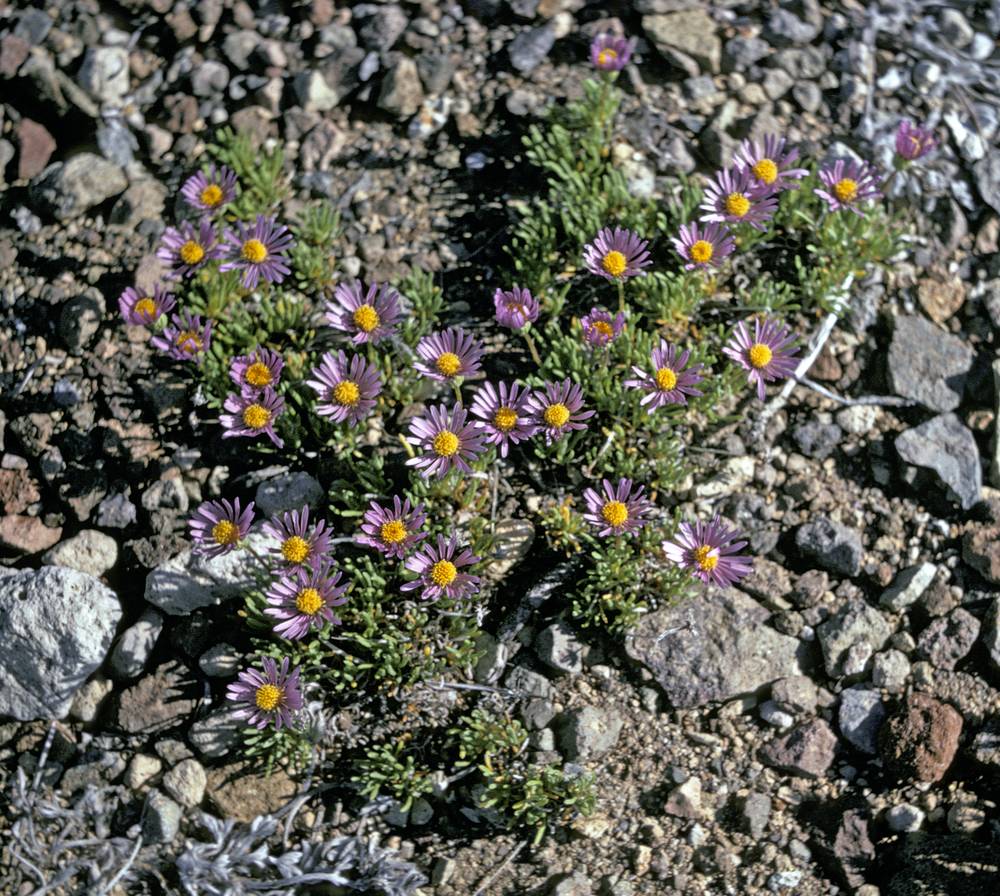
Erigeron elegantulus
Erigeron howellii
dwarf blue fleabane, volcanic fleabane
Howell's fleabane
erect to basally ascending, sparsely to moderately strigose, eglandular.
erect, glabrous to sparsely and minutely strigillose, eglandular.
persistent, linear to filiform, 20–50 × 0.5–1 mm, white, bases sheathing;
margins entire;
tips round to acute or acuminate;
surfaces sparsely to moderately strigose.
persistent, broadly spatulate, 40–150 × 10–35 mm;
margins entire or with few large teeth;
surfaces glabrous, eglandular.
abruptly reduced and usually restricted to basal ? of stem, bases sheathing.
lanceolate to elliptic, 15–80 × 10–35 mm, gradually reduced distally;
margins entire or with few coarse teeth;
surfaces often ciliate or glandular.
3–5 × 8–11 mm.
5–9 × 15–23 mm.
15–30, lavender to purple;
rays 3–8 × 0.7–1.3 mm.
25–50, white;
rays 8–20 × 2.5–4 mm.
corollas 2.5–3.5 mm.
corollas 4–5 mm.
in 3–4 unequal series;
surfaces sparsely strigose, eglandular.
in 2–3 series, with prominent central veins;
surfaces glabrous, densely glandular.
1–2 mm, nearly glabrous to sparsely strigose;
inner pappi of numerous barbellate bristles.
2.5–3 mm, sparsely to moderately strigose;
inner pappi of numerous barbellate bristles.
1, radiate.
1, radiate.
=27.
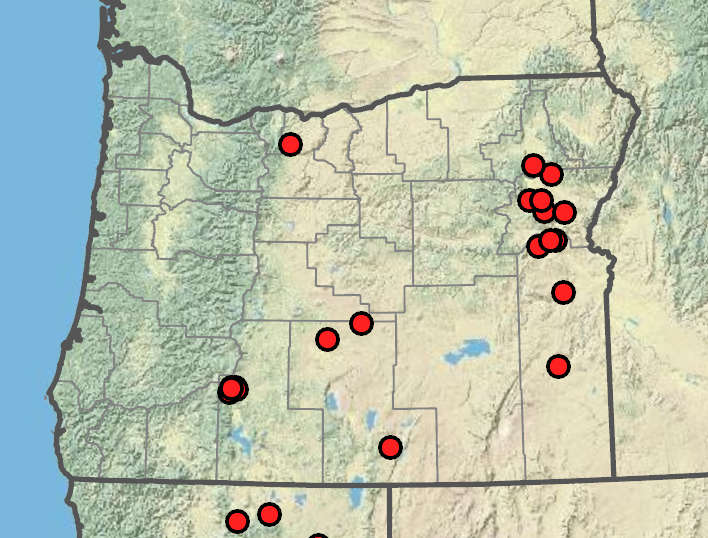
Erigeron elegantulus
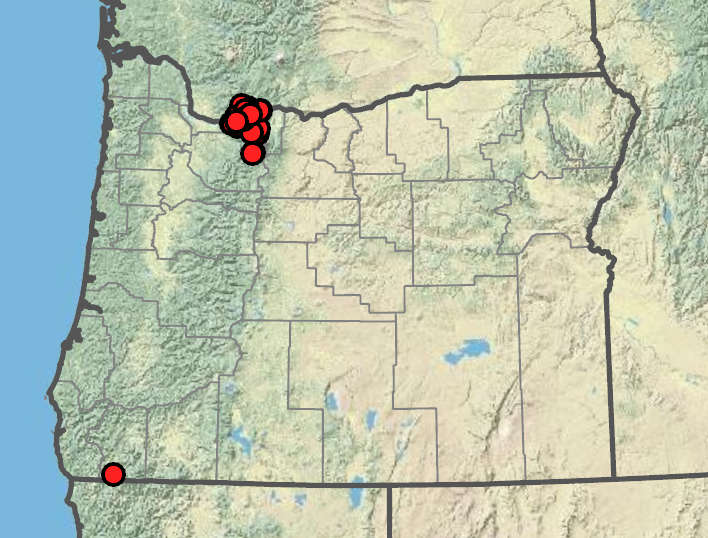
Erigeron howellii
Rocky areas, sagebrush, coniferous forests. Flowering Jun–Aug. 700–2500 m. BR, BW, Casc, Owy. CA. Native.
Rocky slopes, open woods. Flowering May–Jul. 100–1500 m. Casc. WA. Native.
James Riser, Stephen Meyers
James Riser, Stephen Meyers