Eleocharis engelmannii
Eleocharis ovata
Engelmann's spikerush
ovoid spikerush
terete, 2–40 cm × 0.5–1.5(2) mm.
terete, 2–35 cm × 0.3–1 mm.
lanceoloid to subcylindric, 5–10(20) × 2–3(4) mm;
proximal scale empty, encircling approximately 67% of culm; floral scales 25–100(200), 8–12 per mm of rachilla, 2(2.5) × 1–1.3 mm;
apex narrowly rounded to subacute.
ovoid, 2–8 × 2–4 mm; floral scales 25–100+, approximately 10 per mm of rachilla, 1.5–2 × 1 mm; midribs often keeled in distal part of spike;
apex rounded to subacute.
perianth bristles present or often absent; (0)5–8; about as long as the achenes;
anthers 0.3–0.7(1) mm;
stigmas 2–3.
perianth bristles present, rarely absent; (5)6–7, exceeding tubercle;
stamens 2(3);
anthers 0.3 mm;
stigmas 2 or some 3.
biconvex or to 33% greatly compressed trigonous, 0.9–1.1(1.5) × 0.7– 1.1 mm.
biconvex or to 33% greatly compressed trigonous, 0.75–1 × 0.6–0.85 mm.
persistent, apex of distal leaf sheath obtuse to acute, with tooth to 0.3 mm.
persistent, apex of distal leaf sheath obtuse to acute; tooth to 0.2 mm.
depressed, subdeltoid, 0.1–0.3(0.4) × 0.6–0.9(1) mm, 10–40% as high as wide, 25% or less as high as achene, 90% as wide as achene.
deltoid, 0.3–0.5 × 0.3–0.5 mm, 60% to as high as wide, 33–67% as high and 50–75% as wide as achene.
=10.
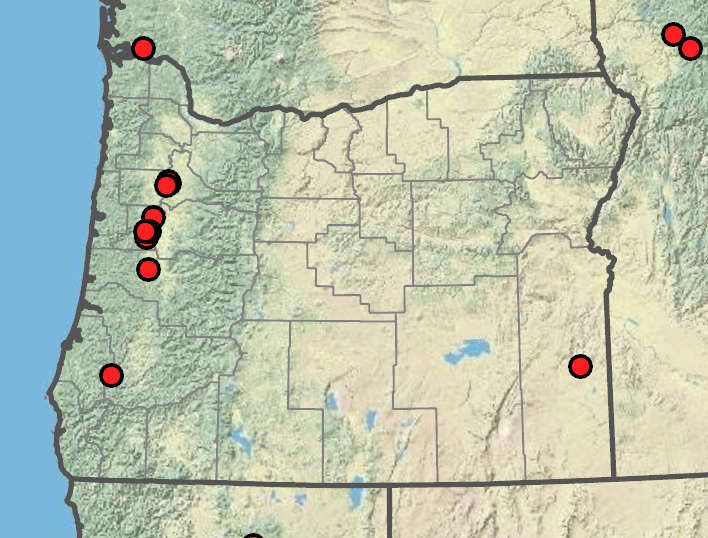
Eleocharis engelmannii
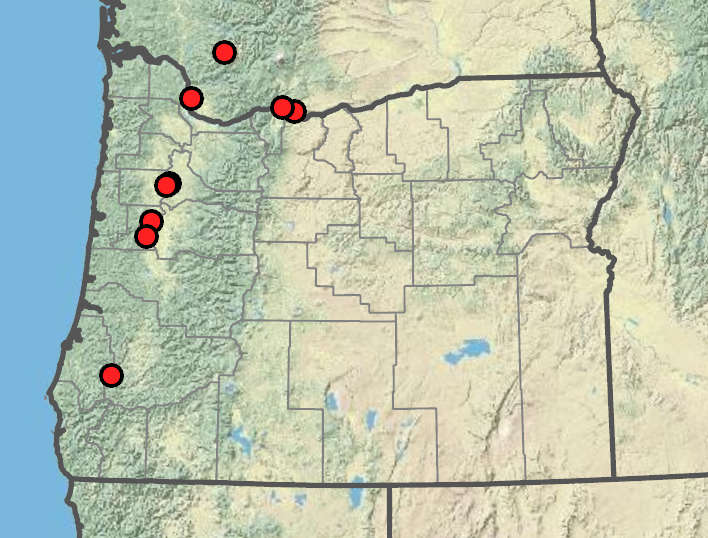
Eleocharis ovata
Freshwater shores exposed by seasonal low water levels, marshes, disturbed wetlands. 50–500 m. WV. CA, ID, WA; north to British Columbia, east to MA, southeast to AL. Native.
Eleocharis engelmannii is similar to E. ovata and the much more common E. obtusa but has markedly shorter tubercles and usually more cylindric spikes.
Freshwater shores exposed by seasonal low water levels, marshes, and disturbed wetlands. 100–1300 m. ECas, Sisk, WV. WA; north to British Columbia; northeastern North America. Native?
Pacific Northwest occurrences of E. ovata are disjunct from the species northeastern North American range. This may suggest that the species is introduced in Oregon. More research is needed.
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search