Eleocharis engelmannii
Cyperaceae
Engelmann's spikerush
sedge family
terete, 2–40 cm × 0.5–1.5(2) mm.
usually triangular, occasionally terete, rarely compressed or quadrangular; solid or pithy.
basal and/or cauline, alternate, usually 3-ranked, bases forming cylindric sheaths enclosing stem;
margins fused;
ligules often present;
blades frequently absent from some basal leaves, rarely from cauline leaves; when present flat, folded, rolled, or terete, linear.
lanceoloid to subcylindric, 5–10(20) × 2–3(4) mm;
proximal scale empty, encircling approximately 67% of culm; floral scales 25–100(200), 8–12 per mm of rachilla, 2(2.5) × 1–1.3 mm;
apex narrowly rounded to subacute.
with a shortened axis; floral scales 1–many, crowded, spirally arranged, sometimes 2-ranked, usually each subtending a single flower or perigynium, sometimes proximal and/or distal scales empty; perigynia if present closed or open down one side, subtending and enclosing a very short rachilla-bearing 1-pistillate flower (Carex), sometimes also (0)3 staminate flowers and empty scales (Kobresia);
spikes aggregated into secondary inflorescences that are panicles, often modified and sometimes consisting of a single spike; secondary inflorescences usually subtended by a foliaceous or scale-like or bristle-like bract.
perianth bristles present or often absent; (0)5–8; about as long as the achenes;
anthers 0.3–0.7(1) mm;
stigmas 2–3.
bisexual (unisexual in Carex and Kobresia);
perianth absent or consisting of (1)3–6(30) bristles and/or scales;
stamens usually (1)3, rarely more;
ovary with 1–3(4) carpels, fused; locule 1;
style undivided or branched;
stigmas 2–3(4).
achenes, usually trigonous or biconvex.
biconvex or to 33% greatly compressed trigonous, 0.9–1.1(1.5) × 0.7– 1.1 mm.
persistent, apex of distal leaf sheath obtuse to acute, with tooth to 0.3 mm.
depressed, subdeltoid, 0.1–0.3(0.4) × 0.6–0.9(1) mm, 10–40% as high as wide, 25% or less as high as achene, 90% as wide as achene.
Eleocharis engelmannii
Cyperaceae
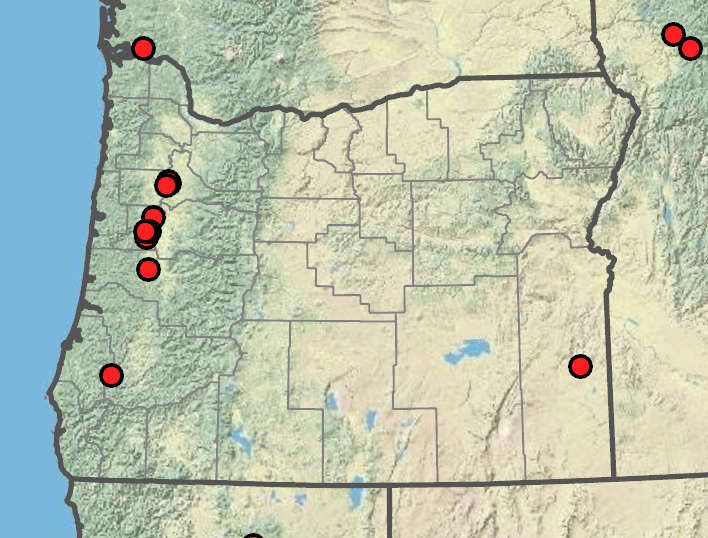
Freshwater shores exposed by seasonal low water levels, marshes, disturbed wetlands. 50–500 m. WV. CA, ID, WA; north to British Columbia, east to MA, southeast to AL. Native.
Eleocharis engelmannii is similar to E. ovata and the much more common E. obtusa but has markedly shorter tubercles and usually more cylindric spikes.
Cosmopolitan. Approximately 100 genera; 16 genera treated in Flora.
Cyperaceae (except Eleocharis) is characterized by unusual holocentric chromosomes, in which spindle fibers attach throughout the length of the chromosome, not at discrete centromeres. Also, reduction of chromosome number occurs at the second division of meiosis. These traits are shared with the related family Juncaceae but not by other vascular plants. Chromosome numbers in sedges are often very high, but it is unclear if this represents polyploidy or fragmentation of holocentric chromosomes. When collecting sedges, get the rhizomes (if present) because some species are distinguished by their cespitose or rhizomatous growth form. If possible, collect extra inflorescences because checking floral traits can be destructive. In some genera, species identification requires mature fruits.
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search
- Local floras:
CA,
OR
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search