Eleocharis bolanderi
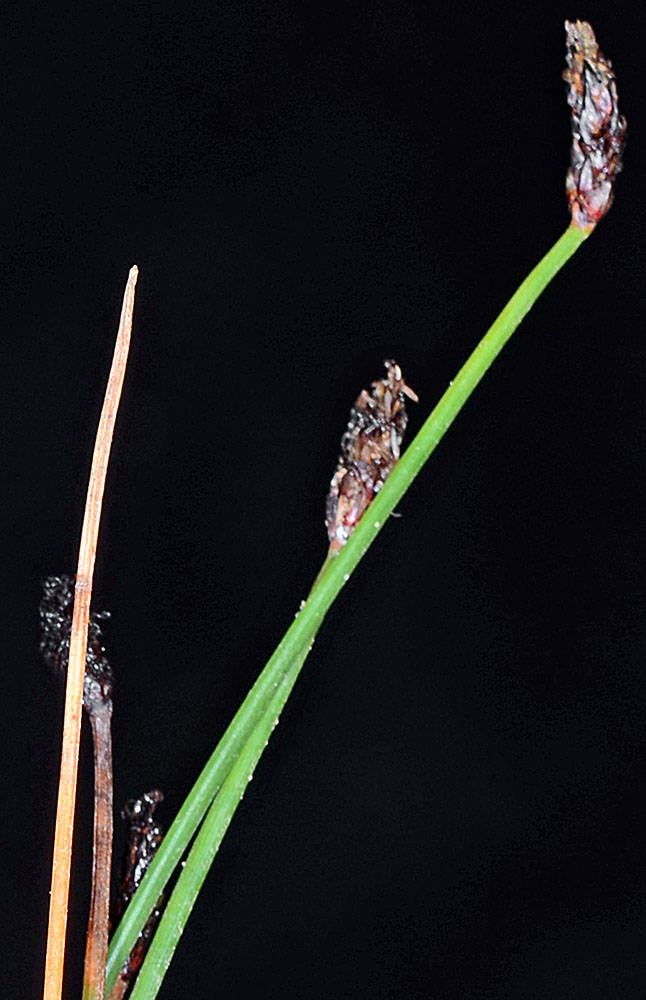
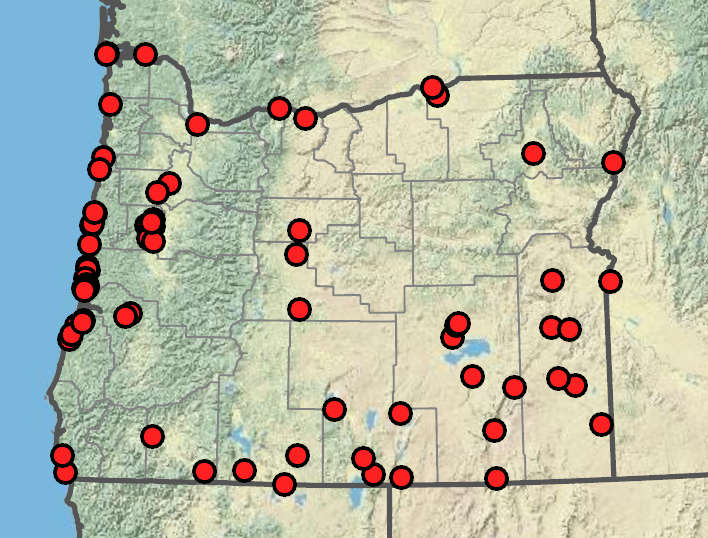
Eleocharis macrostachya
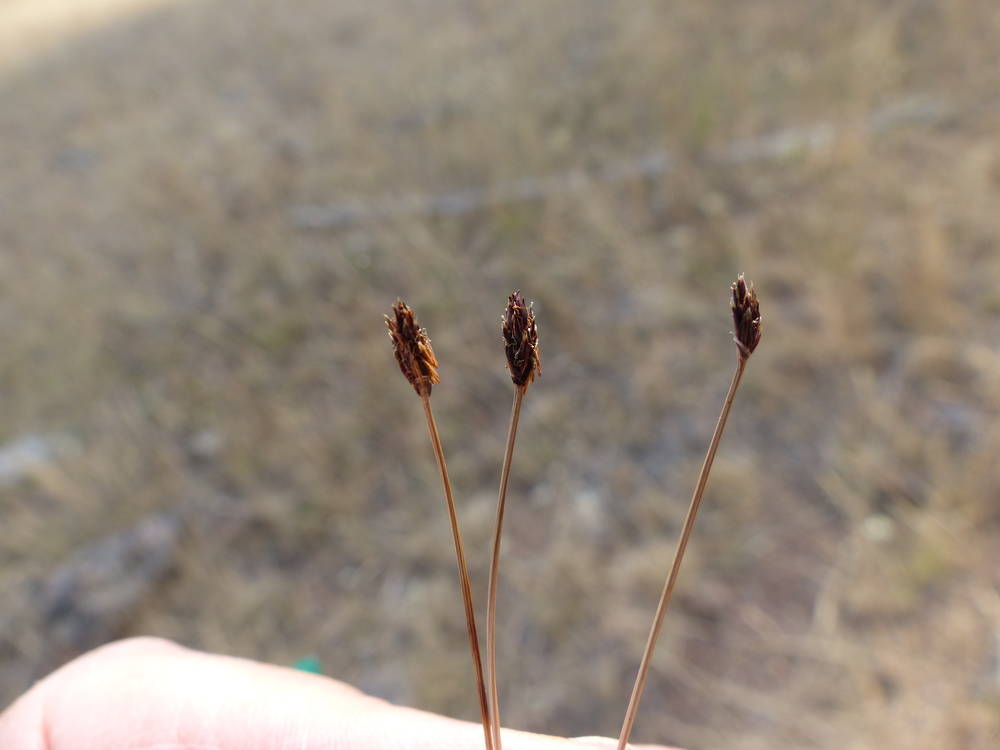
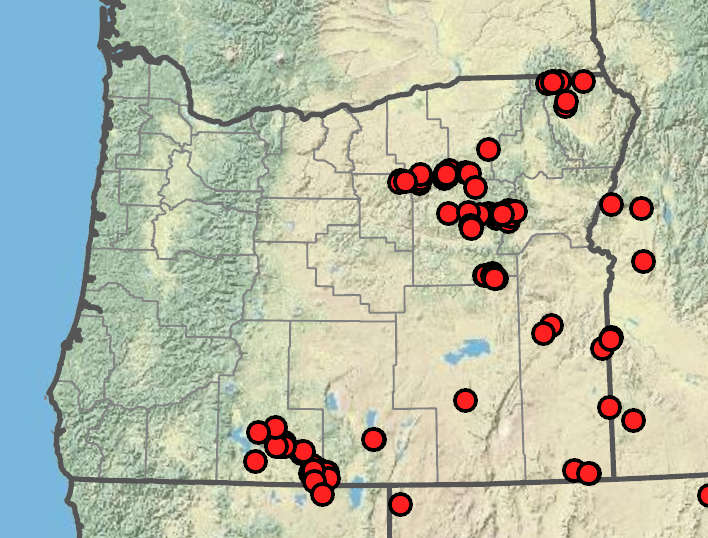
Bolander's spikerush
confusing spikerush, pale spikerush
subterete, 10–30 cm × 0.3–0.5 mm.
terete to markedly compressed; to 3 times wider than thick, 10–100 cm × 0.5–2.5(3.5) mm.
ovoid, 3–8 × 2–3 mm;
proximal scale clasping; entire, subproximal scale with flower; floral scales 8–30, 4–5 per mm of rachilla, 2–3 × 1.5 mm;
apex entire; acute, often keeled in distal part of spike.
narrowly lanceoloid to ovoid, 5–40 × 2–5 mm;
proximal scale clasping (6)75(100)% of culm usually variably in same plant, subproximal scale usually empty in some spikes and subtending a flower in other spikes in the same clone; floral scales 30–80, 3–5 per mm of rachilla, 2.5–5.5 × 1.5–2.5 mm.
perianth bristles 3–6, often unequal; from rudimentary to 50% of achene length;
anthers 0.9–1.4 mm;
stigmas 3.
perianth bristles 4(5), sometimes rudimentary or absent; much shorter than achene to equaling tubercle;
stamens 2(3);
anthers 1.3–2.7 mm;
stigmas 2.
slightly to greatly compressed-trigonous, rarely thickly lenticular, 0.9–1.2 × 0.65–0.8 mm.
biconvex to plano-convex, 1.1–1.9 × 0.8–1.5 mm.
persistent, not splitting;
apex obtuse, rarely hardened, lacking a tooth.
persistent;
apex truncate to obtuse; tooth sometimes present on some or all culms, 0.1–0.6(1) mm.
flat to shallowly pyramidal; lower than wide, 0.1–0.3 × 0.4–0.65 mm.
pyramidal; as high as or sometimes much higher than wide, 0.35–0.7 × 0.25–0.7 mm.
=18, 19, 38.
Eleocharis bolanderi
Eleocharis macrostachya
Shallow, rocky, ephemeral streams. 1100–2100 m. BR, BW, Owy. CA, NV, ID; east to CO. Native.
Eleocharis bolanderi is easily recognized in summer when it forms masses of dry, brown, dormant and apparently dead culms in dry stream beds. It is easily pulled up to expose its cespitose habit. The virtually flat tubercles are particularly distinctive.
Fresh to slightly brackish or alkaline marshes, lake shores, stream beds, vernal pools, deflation plains, and wet meadows. 0–1800 m. BR, BW, Col, CR, ECas, Est, Lava, Owy, Sisk, WV. CA, ID, NV, WA; north to AK, east to Quebec and MS, south to Mexico; South America. Native.
Eleocharis macrostachya is a diploid-polyploid complex consisting (at least in part) of populations that originated as hybrids of E. palustris with E. erythropoda and E. uniglumis. As a result, E. macrostachya is one of the most variable species in the genus. Plants vary from short, narrow-culmed plants resembling E. erythropoda to fairly robust individuals resembling E. palustris. The extent to which the proximal scale clasps the culm is usually greater than in E. palustris and often varies within a clone, as does the present or absence of a flower in the subproximal scale. Strictly coastal individuals have shiny dark chestnut brown or blackish achenes with brownish midribs. The proximal scales usually clasp 95–100% of the culm, and the subproximal scales usually subtend flowers. The culms are tough and sometimes arching. These plants can be referred to as E. macrostachya variant C (coastal form) or E. macrostachya tending toward E. uniglumis, according to Smith et al. (2002). Most inland Oregon plants are referred to as E. m. variant B.
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
- Local floras:
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search