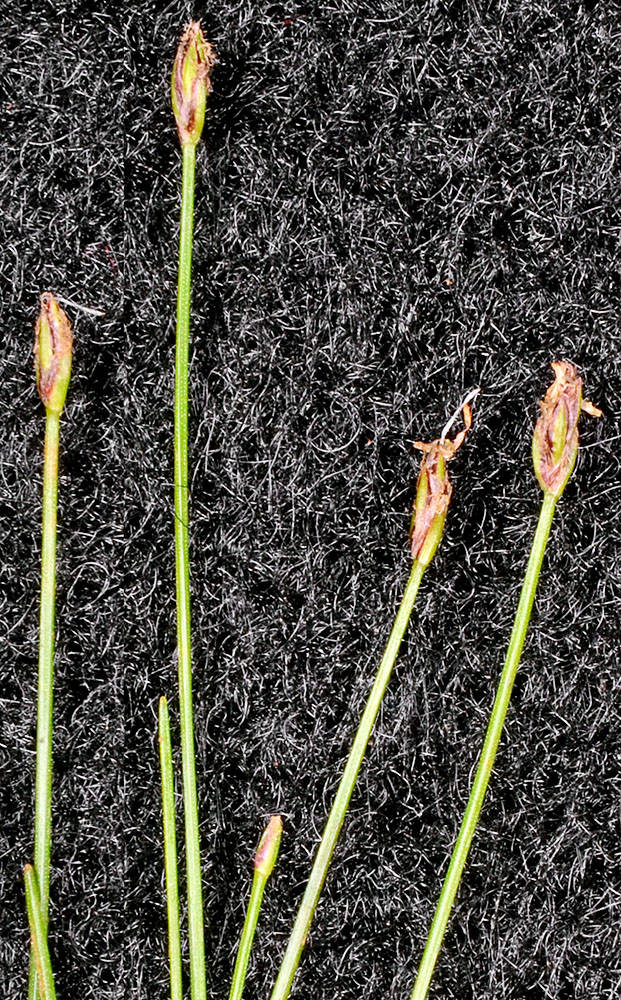
Eleocharis acicularis
Eleocharis parishii
needle spikerush
Parish's spikerush
sometimes arching; terete to sometimes distinctly compressed, 1–60 cm × 0.2–0.5(0.7) mm.
terete or cross section elliptic (or rectangular), 10–50 cm × 0.2–0.7(1) mm.
2–8 × 1–2 mm; floral scales 4–25, 4–6 per mm of rachilla, 1.5–2.5(3.5) × 1–1.5 mm;
apex blunt to acute.
narrowly lanceoloid, 3–20 × 1.5–2.5 mm;
proximal scale amplexicaul; entire, subproximal scale empty or with flower; floral scales 15–40, 3–4 per mm of rachilla, 2–3 × 1 mm;
apex entire, rounded to obtuse in proximal part of spike; acute in distal part, keeled; at least in distal part of spike.
perianth bristles mostly absent, uncommonly 2–4; shorter than to equaling achene;
anthers 0.7–1.5 mm;
stigmas 3.
perianth bristles (0)3–7, often unequal; rudimentary to slightly exceeding tubercle;
anthers 1.1–2 mm;
stigmas 3.
with angles plus about 8–12 obscure to prominent longitudinal ridges, narrowly to broadly obovoid to obpyriform, 0.7–1.1 × 0.35–0.6 mm; fine horizontal ridges 30–60, clearly evident to crowded and obscure; spaces between trabeculae sometimes translucent.
compressed-trigonous, 0.8–1.4 × 0.5–0.7 mm.
often splitting;
apex rounded (to acute).
persistent, not splitting;
apex with tooth often present on most or all culms; to 1 mm.
pyramidal to much depressed; (0.05)0.1–0.2 × 0.15– 0.25 mm.
pyramidal, often higher than wide, 0.3–0.4 × 0.25–0.35 mm.
=20.
=10.
Eleocharis acicularis
Eleocharis parishii
Ponds, shallow wetlands, and exposed shorelines and mudflats, vernal pools, and other, often disturbed wetlands. 0–2300 m. All ecoregions except Col. CA, ID, NV, WA; north to AK, east to Greenland and GA, south to South America; Australia, Eurasia. Native.
Plants of this species frequently grow as submerged or floating mats that do not flower. These plants differ from typical E. acicularis in having terete, smooth, soft, translucent culms with conspicuous partitions between the air cavities. Such plants are difficult to identify and can be confused with Schoenoplectus subterminalis. Eleocharis acicularis is highly variable, but much of the variation is probably environmental, dependent particularly on water depth. As a result of this plasticity, recognition of any of the described varieties is likely unwarranted. Eleocharis bella is similar but annual, cespitose, only occasionally produces rhizomes and has smaller floral scales, anthers, and achenes.
Fresh to brackish wetlands, often on drying lake shores, pond margins, streamsides and springs. 200–500 m. Sisk. CA, NV; east to Kansas, south to Mexico. Native.
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search