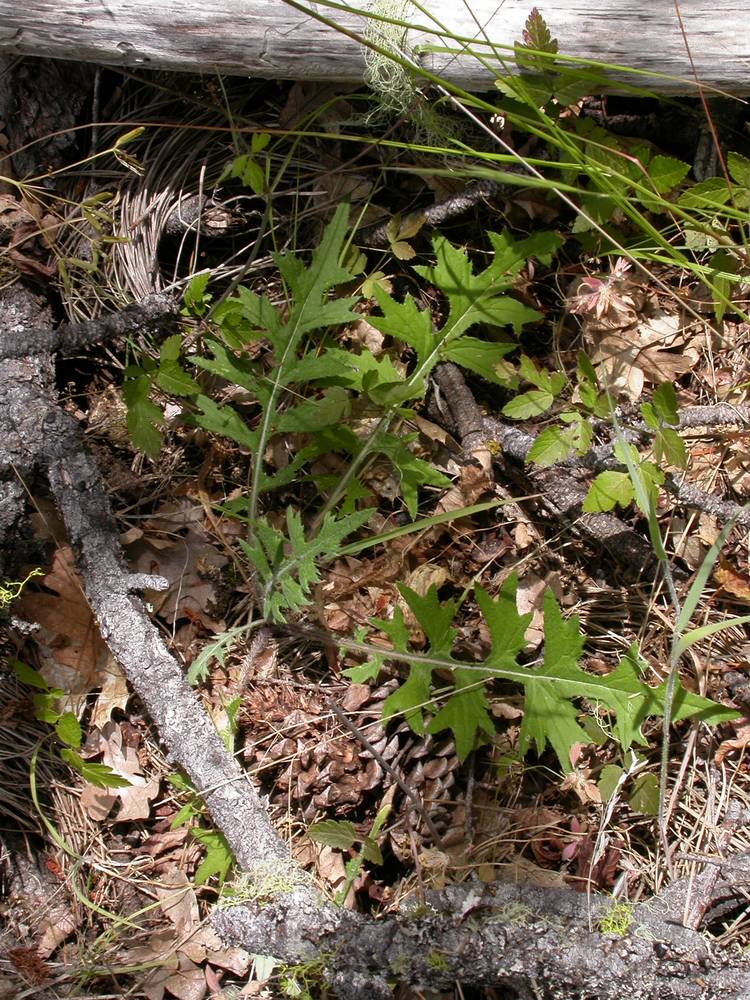
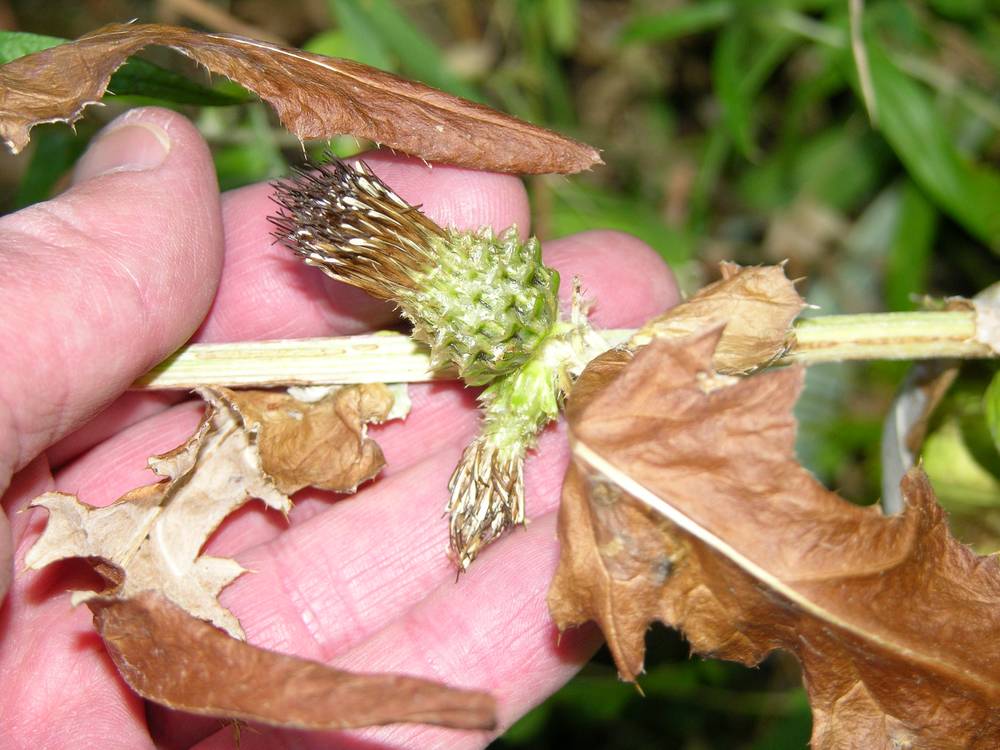
Cirsium remotifolium
Cirsium
few-leaved thistle, weak thistle
thistle
usually 1; slender, arachnoid-villous, sometimes thinly so.
erect, branched or simple, sometimes spiny-winged.
linear-oblong to elliptic, 7–35 × 1–15 cm;
margins entire to dentate or pinnately lobed;
lobes triangular-ovate to linear;
spines fine, 1–6 mm;
surfaces abaxially thinly to densely tomentose, adaxially glabrate to thinly arachnoid-villous;
basal occasionally present at flowering, sessile, clasping, or petiolate.
basal and cauline, alternate;
margins entire to deeply toothed or pinnately lobed;
lobes and teeth usually spiny.
heads solitary at branch tips or distal axils, or in raceme- or panicle-like arrays.
hemispheric to campanulate, 1–2.5 × 1.5–3.5 cm, glabrous to thinly arachnoid-villous.
flat to convex; very bristly;
paleae 0.
corollas 16–25 mm, cream-colored to purple;
tubes 6–12 mm;
throats 5–10.5 mm;
lobes 3.5–8 mm;
styles conspicuously exserted;
tips 4–6 mm.
corollas bilateral, white or cream-colored to pink, red, or purple;
style tips elongate.
subequal to strongly imbricate, sometimes with inconspicuous glutinous ridges;
spines 1–6 mm; outer bases ? 2 mm wide.
many in 5–20 series, imbricate or not;
margins usually entire or occasionally scarious, ciliate-spiny, or erose;
midveins sometimes with glutinous ridges.
4.5–5.5 mm, tan to dark brown;
pappi 12–25 mm.
compressed; ovoid, tan to dark brown, glabrous, attachment scar off-center;
pappi in 3–5 series, persistent or deciduous in rings.
few–many.
discoid, pedunculate or sessile.
Cirsium remotifolium
Cirsium
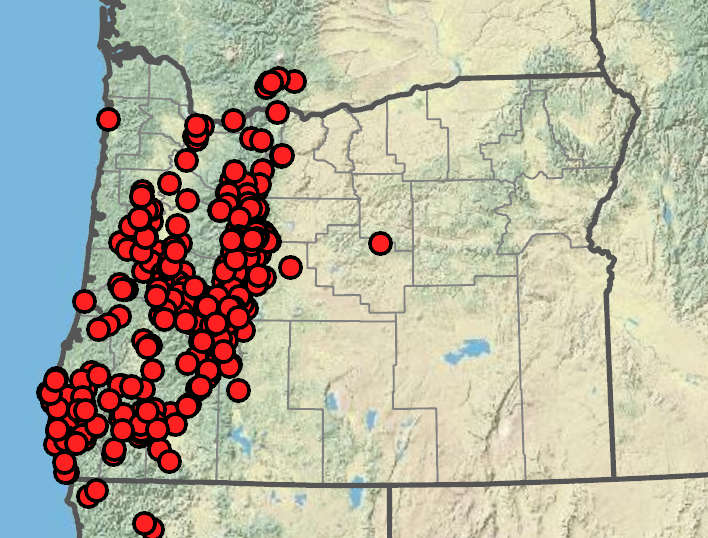
Western United States. 3 varieties.
Cirsium remotifolium is known to form fertile hybrids with C. edule where their ranges overlap.
Africa, Asia, Europe, North America. ~200 species; 15 species treated in Flora.
The taxonomy of Cirsium is complicated by hybridization and a high level of morphological variation within species. Style tips are measured including the somewhat swollen nodes and fused portions of style branches. Cirsium ochrocentrum var. ochrocentrum has been collected once in Oregon (2013) but does not appear to be naturalized.
Bridget Chipman
Bridget Chipman
- Local floras:
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search