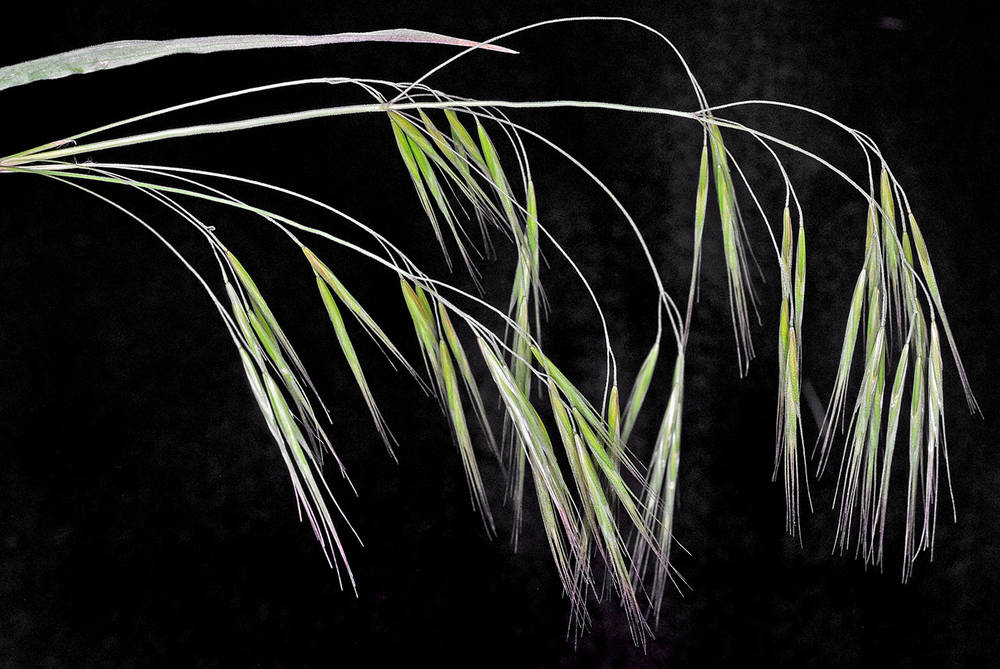
Bromus tectorum
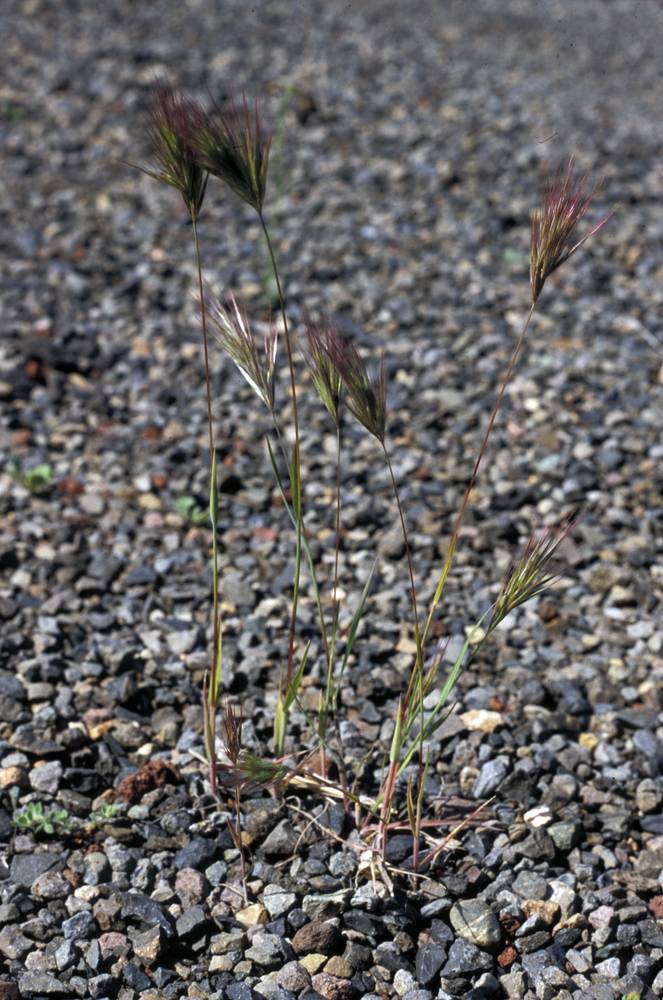
Bromus rubens
cheatgrass, downy brome, downy chess
foxtail chess, red brome
puberulent.
often puberulent.
sheaths densely and softly retrorsely pubescent to pilose; upper sheaths sometimes glabrous;
blades 1–16 cm × 1–6 mm, softly hairy on both surfaces.
sheaths softly pubescent to pilose;
blades 1–15 cm × 1–5 mm, pubescent on both surfaces.
5–20 × 3–8 cm; open, nodding;
branches 1–4 cm, drooping, 1-sided and longer than the spikelets, usually at least 1 branch with 4–8 spikelets.
2–10 × 2–5 cm; erect; dense, often reddish brown;
branches 0.1–1 cm, ascending, never drooping, not readily visible, 1–2 spikelets.
10–20 mm, moderately laterally compressed, not densely crowded, 4–8 florets.
18–25 mm; much longer than the panicle branches, densely crowded, subsessile, moderately laterally compressed, with 4–8 reddish florets.
villous, pubescent, or glabrous;
lower glumes 4–9 mm, 1-veined;
upper glumes 7–13 mm, 3–5-veined.
pilose;
lower glumes 5–8 mm, 1(3)-veined;
upper glumes 8–12 mm, 3–5-veined.
9–12 mm, lanceolate, glabrous or pubescent to pilose, 5–7-veined;
tips acuminate; hyaline; bifid, with teeth 0.8–2(3)mm, awned;
lemma awns 10–18 mm; straight.
10–15 mm, linear-lanceolate, pubescent to pilose, 7-veined;
margins hyaline;
tips acuminate, with teeth 1–4 mm, awned;
lemma awns 8–20 mm; straight.
0.5–1 mm.
0.5– 1 mm.
=14.
=14, 28.
Bromus tectorum
Bromus rubens
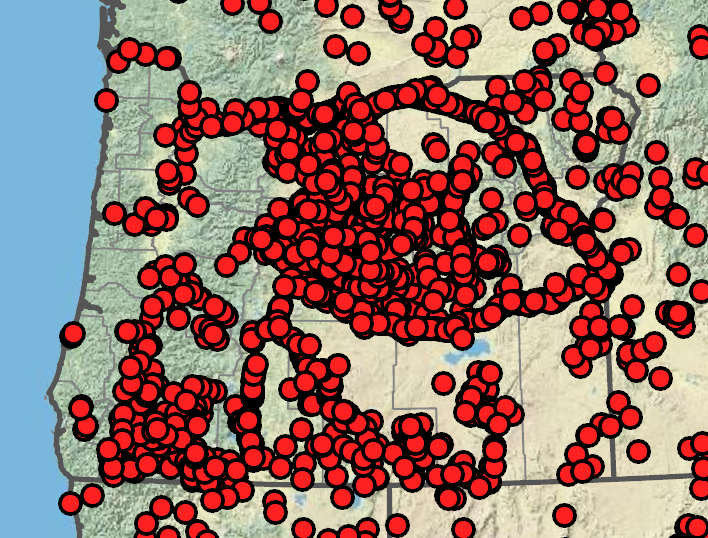
Disturbed areas, sagebrush steppe, degraded grasslands, roadsides. 0–2400 m. BR, BW, Casc, Col, CR, ECas, Lava, Owy, Sisk, WV. CA, ID, NV, WA; throughout North America; worldwide. Exotic.
Bromus tectorum is a relatively short grass with drooping inflorescences. Similar B. sterilis and B. diandrus have longer glumes, lemmas, and awns, and spikelets that hang down at a shallower angle than those of B. tectorum. The introduction of B. tectorum to shrub steppe habitats during a time of massive overgrazing in the late 1800s has made restoration of native plant communities difficult or impossible, even where grazing no longer occurs. Fast-growing B. tectorum seedlings outcompete slower growing native grass seedlings for water in drying soils. At maturity, the awns make B. tectorum unpalatable to livestock.
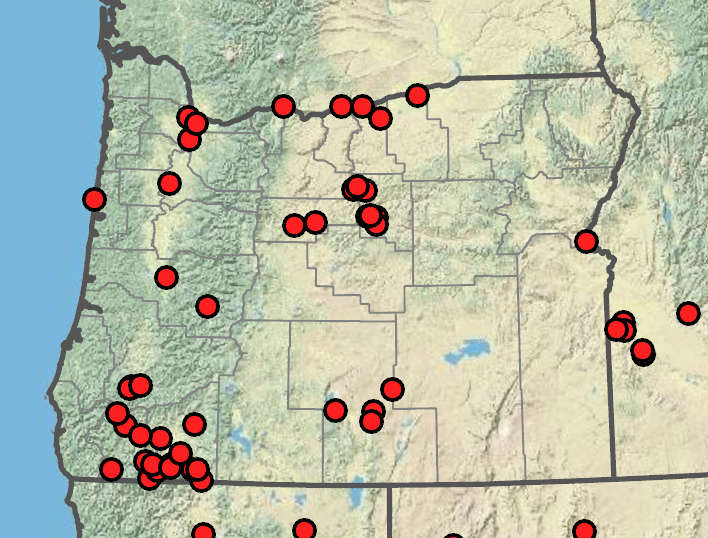
Disturbed places, bare droughty soils. 0–1400m. BR, Casc, Col, Est, Lava, Owy, Sisk, WV. CA, ID, NV, WA; east to CO and TX; MA, NY; Europe. Exotic.
Similar B. diandrus and B. sterilis usually have nodding inflorescences with the spikelets angling down and much more open inflorescences. Bromus madritensis is very similar to B. rubens with which it is sometimes considered conspecific. Bromus madritensis was collected once on ballast in Portland in 1912 and apparently did not persist. It has a somewhat looser inflorescence with longer, exposed, erect panicle branches.
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
Barbara Wilson, Richard Brainerd, Nick Otting
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search