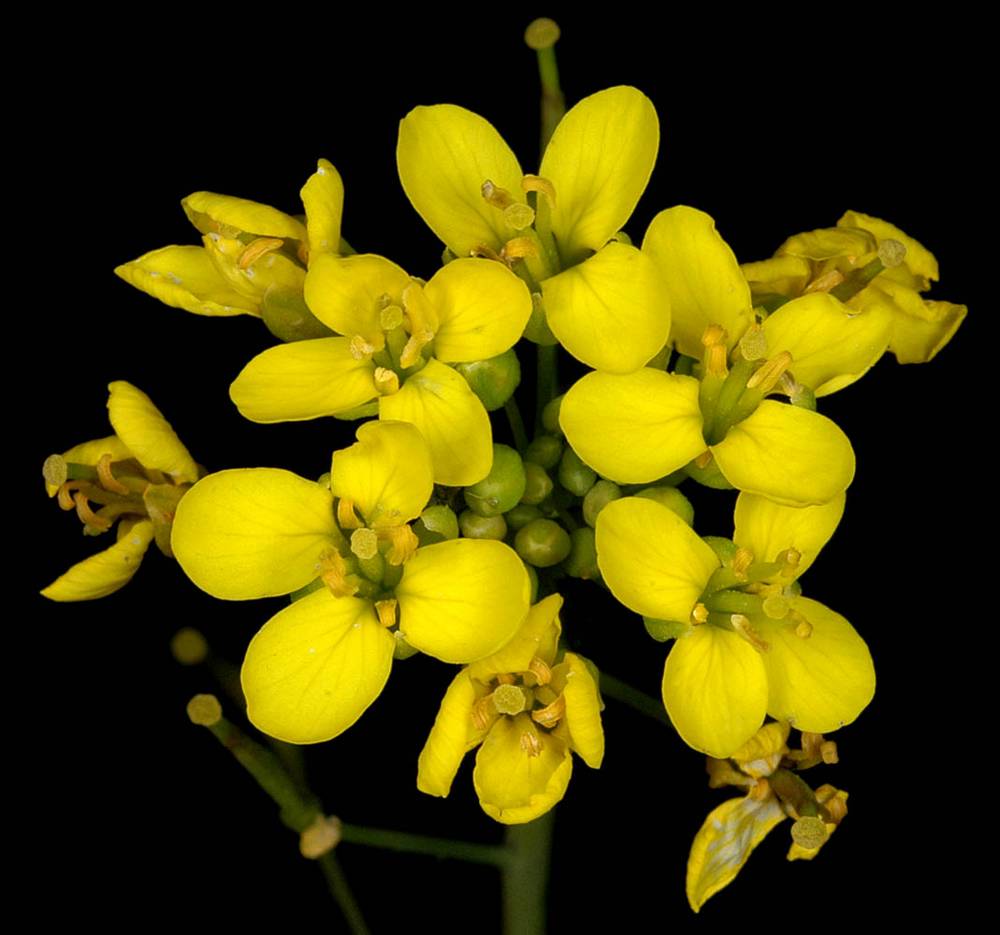
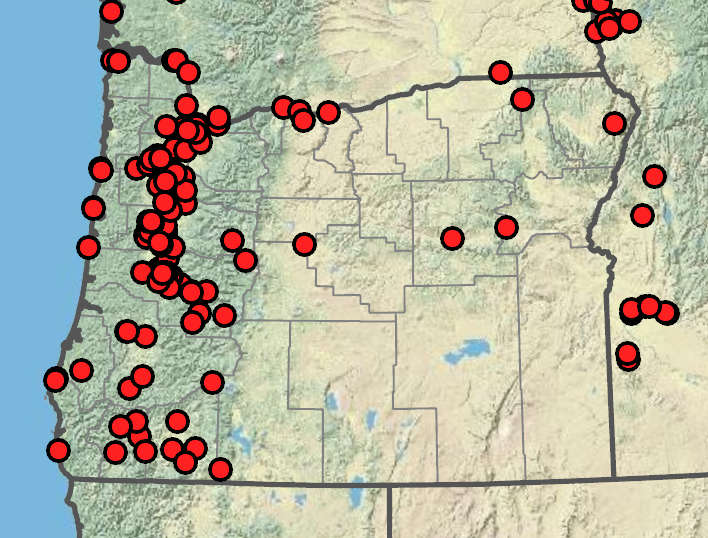
Brassica rapa
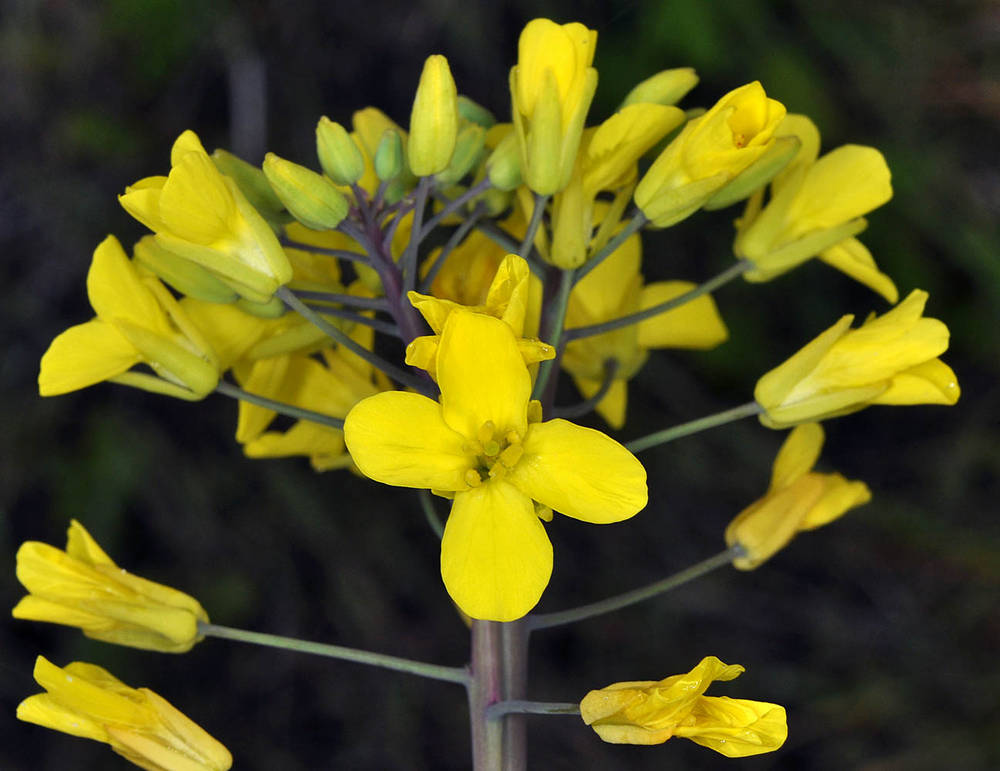
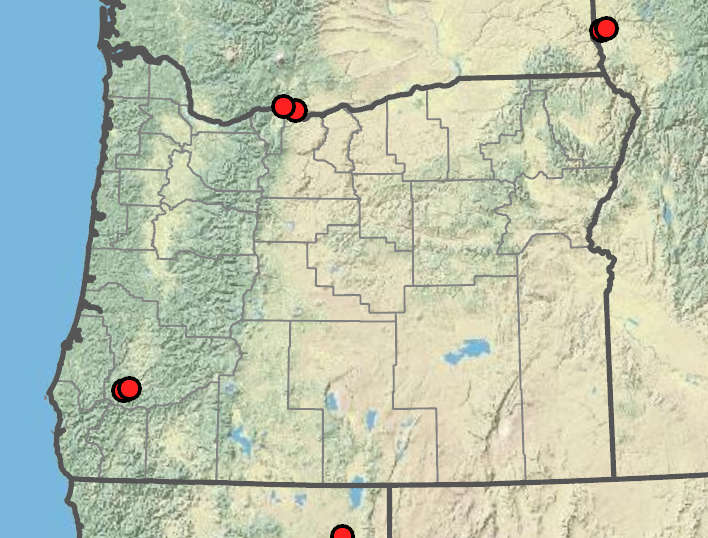
Brassica napus
field mustard, turnip
canola, rapeseed, rutabaga
3–12(19) dm.
3–15 dm.
and lowermost cauline (5)10–40(60) × 3–10 (20) cm;
margins entire, dentate, or pinnatisect, with terminal lobes larger than 1–6 lateral lobes on each side, petiolate.
and lowermost cauline 5–25(40) × 2–7(10) cm;
margins pinnately lobed, lyrate, or undivided; entire or dentate; terminal lobes larger than 1–6 lateral lobes on each side, petiolate.
fruiting pedicels ascending to divaricate; (5)10–25(30) mm.
fruiting pedicels divaricate; (10)12–23(30) mm.
sepals oblong; (3)4–6.5(8) mm, ascending;
petals obovate; (5)7–10(13) × (2.5)3–6(7) mm, bright yellow, rarely pale or whitish yellow;
claws 3–7 mm;
anthers oblong, 1.5–2 mm;
filaments 4–6(7) mm;
lateral curved at base;
styles obsolete.
not overtopping buds;
sepals ascending, oblong; (5)6–10 mm;
petals obovate; (9)10–16(18) × (5)6–9(10) mm; bright or pale yellow;
claws 5–9 mm;
filaments (5)7–10 mm;
lateral curved at base;
styles obsolete.
divaricate to ascending; terete; (2)3–8(11) cm × 2–4(5) mm, valvular segments (1.3)2–5(7.5) cm, 8–15-seeded per locule;
valves with prominent midveins; terminal segments conical; (0.3)1–2.5(3.5) cm; seedless or rarely 1-seeded, sessile.
divaricate to ascending; terete or slightly 4-angled; (3.5)5–9.5(11) cm × (2.5)3.5–5 mm, valvular segments (3)4–8.5(9.5) cm, 12–20(30)-seeded per locule;
valves with prominent midvein, slightly torulose or smooth; terminal segments conical; (0.5)0.9–1.6 cm; seedless or 1-seeded.
1–1.8 mm in diameter.
(1.2)1.5–2.5(3) mm in diameter.
ovate to lanceolate, 2–8(12) × 0.8–3 cm, bases amplexicaul or auriculate, sessile.
to 8 × 3.5 cm, bases amplexicaul or auriculate, sessile.
=20.
=38.
Brassica rapa
Brassica napus
Abandoned fields, roadsides, disturbed areas, gardens. Flowering Apr–Oct. 0–1500 m. BW, Casc, Col, CR, Est, Lava, Sisk, WV. CA, ID, NV, WA; worldwide. Exotic.
Brassica rapa includes many cultivars. These are recognized as varieties or subspecies, including turnip (ssp. rapa), Chinese mustard or bok choy (ssp. chinensis), and Chinese cabbage or petsai (ssp. pekinensis).
Roadsides, disturbed areas, waste places, cultivated and abandoned fields, garden escape from cultivation. Flowering May–Sep. 0–800 m. Sisk. CA, ID, NV, WA; worldwide. Exotic.
Brassica napus is an allotetraploid derived from hybridization between the B. oleracea complex (n=9) and B. rapa (n=10). It is widely cultivated worldwide for canola seed oil.
Ihsan Al-Shehbaz
Ihsan Al-Shehbaz
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria,
Turner Photog.
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search