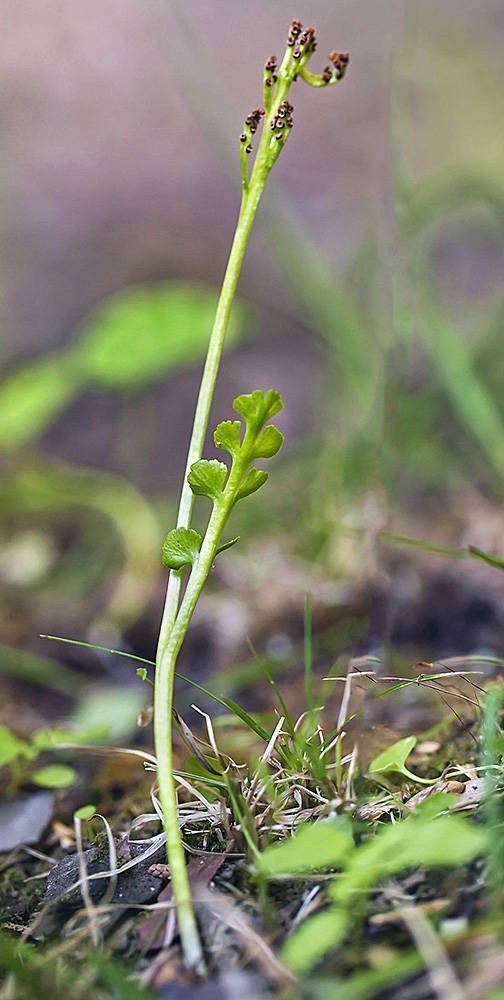
Botrychium crenulatum
crenulate moonwort, dainty moonwort
45(40–48) μm.
well developed; greater than 3 cm, green.
stalk (1)5(17) mm long;
blade 1-pinnate; ovateoblong to linear-oblong; to 6.5 × 1.8 cm (averaging 2 cm long), yellow-green, usually with a thin, herbaceous texture;
pinnae in (2)3(5) pairs, overlapping or not, spreading at nearly a right angle to rachis; fan-shaped, spanning an arc of 60–150(180)°; broadest at the outer margin, usually finely crenulate and sometimes with 1–5 incisions.
erect;
stalk 0.5–2 times as long as the trophophore at spore release;
branches well developed, usually spreading or twisted downwards.
=90.
Botrychium crenulatum
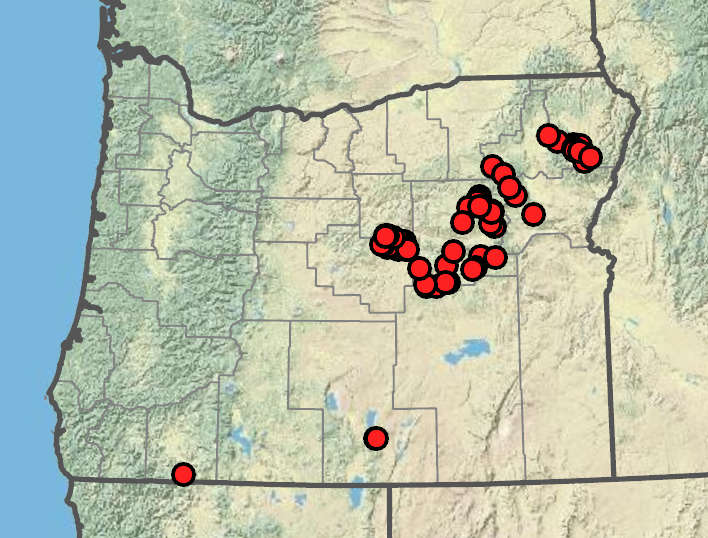
Moist to saturated soils in or near seeps, fens, or on the margins of small streams, usually among low, dense herbaceous cover, from mid-montane to subalpine elevations. 1200–2100 m. BR, BW. CA, ID, NV, WA; western North America. Native.
Botrychium crenulatum grows in more saturated substrates than most other moonworts. It is frequently confused with B. minganense, from which it can usually be distinguished by the two to five pairs of fan-shaped, spreading pinnae with finely crenulate margins, thinner texture, and spreading or downwardpointing sporophore branches. However, many plants do not exhibit all of these characters.
Ben Legler
- Local floras:
BC,
CA,
OR,
WA
- Local Web sites:
CalFlora,
CalPhotos,
Flora NW,
PNW Herbaria
WildflowerSearch
iNaturalist (observations)
USDA Plants Database
- LBJ Wildflower Center
- SEINet
- Plants of the World Online
- Encyclopedia of Life
- Wikipedia
- Google Image Search