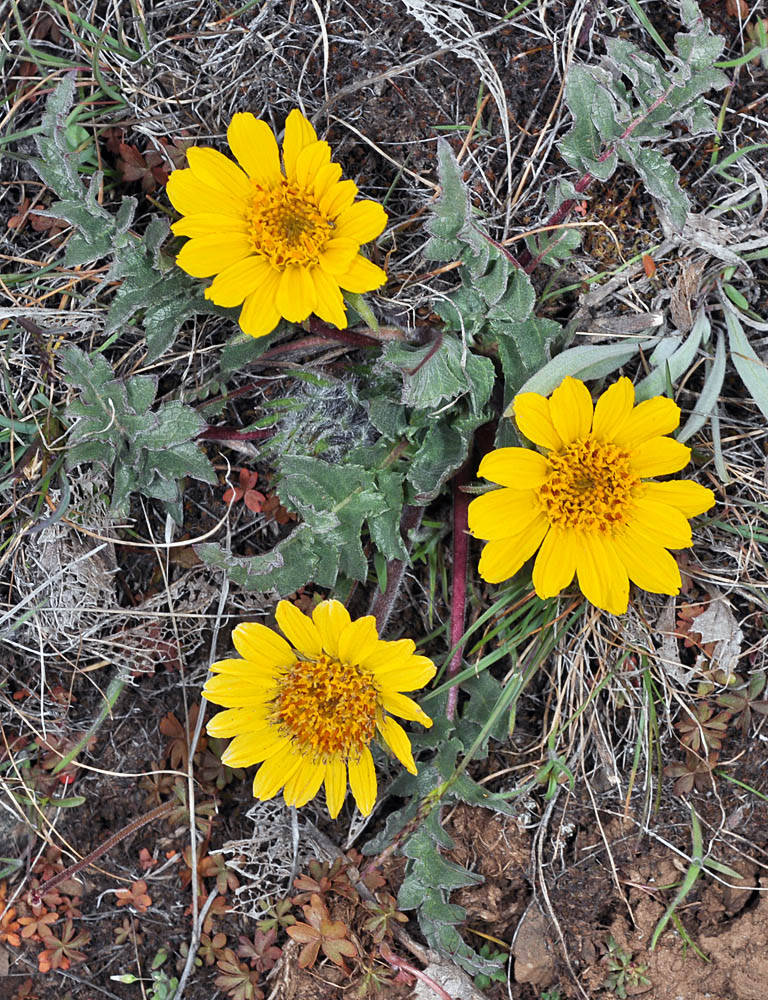
Balsamorhiza serrata
Balsamorhiza hookeri
serrate balsamroot
Hooker's balsamroot
5–34 cm, sparsely villous-tomentose; from single taproot.
11–47 cm; hirsute; from single taproot.
ovate-lanceolate, undivided to pinnatifid, rarely with some leaves pinnately compound;
margins sharply serrate;
tips apiculate;
surfaces sparsely hispid;
basal leaves in 1–few rosettes;
blades 4.5–15 × 2–5.5 cm;
pinnae (when present) 4–11 mm wide;
petioles 1–9(13) cm, often one or more bract-like basal leaves present;
cauline leaves of 1 pair (when present); opposite;
blades 1–4(5.5) × 0.6–1.5 cm;
petioles 2–5.5(6.5) cm.
lanceolate to ovate-lanceolate, 1-pinnately divided with some pinnae toothed or lobed to 3-pinnately lobed;
margins entire to crenate or serrate;
surfaces hirsute to hirsute-sericeous;
basal leaves in 1–few rosettes;
blades 12–24 × 4–12 cm;
pinnae 1–10 mm wide;
petioles 4–15 cm;
cauline blades 3–14.5 × 0.6–4 cm;
petioles 4–11 cm.
with 1 terminal head.
with 1 terminal head.
13–15 × 10–30 mm.
8–15 × 15–25 mm.
8–21, yellow;
rays 13–24 × 4–9 mm.
deciduous, 10–17, yellow;
rays 15–30 × 4–7 mm.
~8 mm.
~6 mm.
linear-lanceolate, 11–18 × 2–4 mm;
tips acuminate, sparsely to densely villous-tomentose.
linear-lanceolate to ovate, 13–20 × 3–6 mm, with or without long-acuminate tips, villous-hirsute and ciliate, sometimes glabrous proximally.
6–7 × 1.5–2 mm, glabrous.
6.5 × 1.5 mm, glabrous.
11–12 mm.
11–12 mm.
=38.
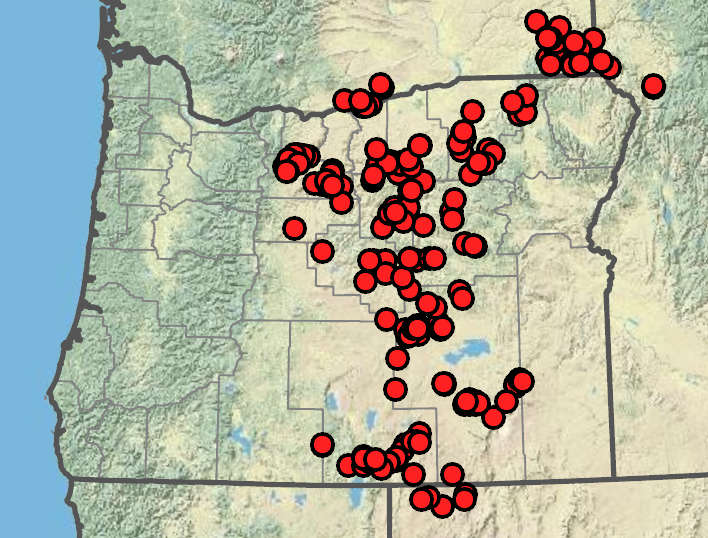
Balsamorhiza serrata
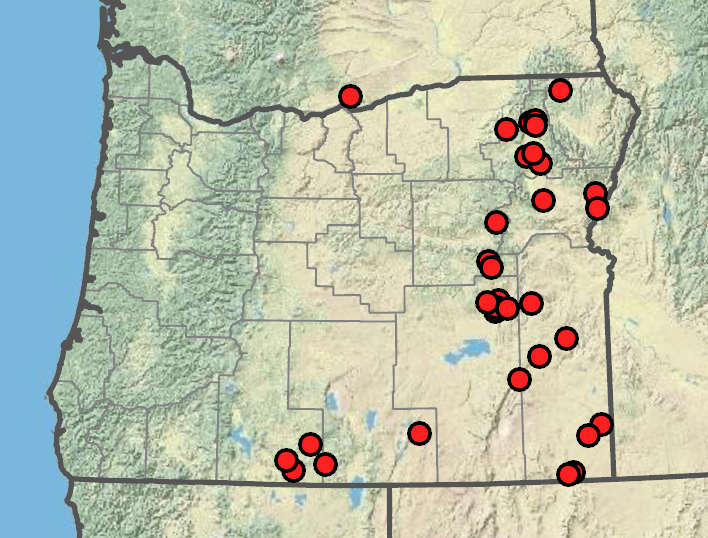
Balsamorhiza hookeri
Dry open areas, serpentine. Flowering Apr–Jun. 600–2100 m. BR, BW, Col, ECas, Lava. CA, NV, WA. Native.
Balsamorhiza serrata is distinct among members of the genus Balsamorhiza in generally having simple leaves with serrate margins and tapered (not sagittate) bases. Some plants have pinnately divided leaves. Further work may show that these plants are actually hybrids between B. serrata and B. hookeri or B. hispidula. Balsamorhiza serrata is known to hybridize with B. sagittata.
Dry, open, often rocky areas. Flowering Apr–Jun. 1000–1600 m. BR, BW. CA, ID, NV, WA; southeast to UT. Native.
As treated here, B. hookeri consists of the members of section Balsamorhiza that are left over after the entities that are distinct in at least some parts of their ranges are removed. Balsamorhiza hookeri hybridizes with B. hispidula and B. sagittata. The species is named after the British botanist William Jackson Hooker, who initially described it as Heliopsis balsamorhiza and tentatively proposed (but did not validly publish, as he did not accept it) the genus Balsamorhiza under the supposition that it would prove to be distinct from Heliopsis once better material was collected.
Abigail (Abby) Moore
Abigail (Abby) Moore