Abies magnifica x Abies procera
(synonym of Abies magnifica)
Abies magnifica x Abies procera
(synonym of Abies magnifica x abies procera)
Shasta red fir
Shasta red fir
usually 1-ranked, occasionally 2-ranked on lower branches, curving upward; flexible;
cross section 4-sided, occasionally 3-sided, 2–3.5 cm × 2–2.5 mm;
abaxial surface bluish green, glaucous, with 8–10 stomatal rows;
adaxial surface bluish green, glaucous, often with 2 whitish bands, not or weakly grooved, 8–10 stomatal rows;
apex rounded to acute.
usually 1-ranked, occasionally 2-ranked on lower branches, curving upward; flexible;
cross section 4-sided, occasionally 3-sided, 2–3.5 cm × 2–2.5 mm;
abaxial surface bluish green, glaucous, with 8–10 stomatal rows;
adaxial surface bluish green, glaucous, often with 2 whitish bands, not or weakly grooved, 8–10 stomatal rows;
apex rounded to acute.
purple.
purple.
14–16 × 5–7 mm, red;
wings approximately same length as body.
14–16 × 5–7 mm, red;
wings approximately same length as body.
to 2.5 m in diameter;
bark gray; smooth, bark of lower trunk deeply furrowed with reddish plates;
branches ascending in crown, descending lower;
twigs opposite to whorled, pubescent 1st year, glabrous after 1st year.
to 2.5 m in diameter;
bark gray; smooth, bark of lower trunk deeply furrowed with reddish plates;
branches ascending in crown, descending lower;
twigs opposite to whorled, pubescent 1st year, glabrous after 1st year.
oblong-cylindrical, 15–20 cm long, purple to greenish brown;
scales pubescent;
bracts exserted and reflexed over scales, covering less than 85% (often much less) of cone at maturity.
oblong-cylindrical, 15–20 cm long, purple to greenish brown;
scales pubescent;
bracts exserted and reflexed over scales, covering less than 85% (often much less) of cone at maturity.
Abies magnifica x Abies procera
Abies magnifica x Abies procera
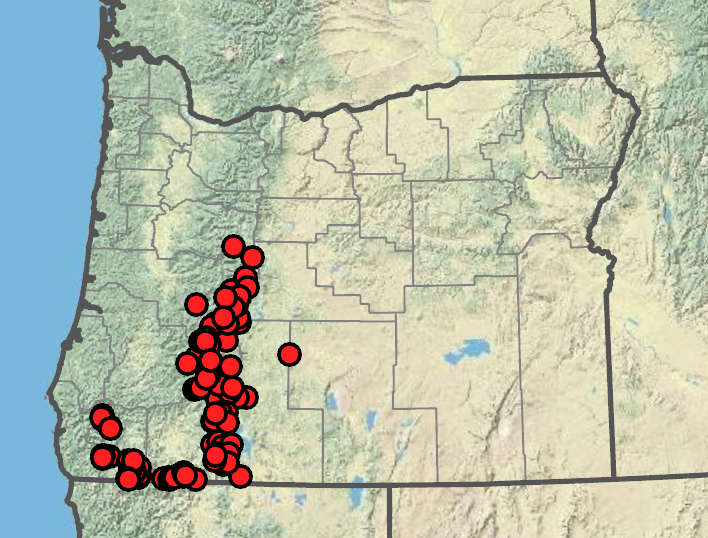
Mid-elevation to subalpine forests. 300–2000 m. Casc, CR. CA, WA. Native.
Morphological and DNA evidence indicates that no pure Abies magnifica is likely to exist in Oregon. As a result, all previously described populations of A. magnifica are now assigned to A. magnifica × A. procera. Specimens of A. magnifica × A. procera can be distinguished from pure A. procera by seed cone and seed cone bract morphology.
Mid-elevation to subalpine forests. 300–2000 m. Casc, CR. CA, WA. Native.
Morphological and DNA evidence indicates that no pure Abies magnifica is likely to exist in Oregon. As a result, all previously described populations of A. magnifica are now assigned to A. magnifica × A. procera. Specimens of A. magnifica × A. procera can be distinguished from pure A. procera by seed cone and seed cone bract morphology.
Stephen Meyers
Stephen Meyers